Introduction:

Sir. I desire to bring under the notice of our authorities and your readers the splendid status of the Malvern Tramways Band, and that public interest may be awakened with a view to sending the Australia’s champion band to contest against England’s best at the famous Crystal Palace brass band contest in London. Our soldiers and sailors, actors and singers, riflemen, footballers and politicians have won fame for Australia, and I feel confident our bandsmen can add fresh lustre to our laurels, and at the same time advertise our resources. The time is opportune to show the mettle of our pasture on the English contest platform, where the best in the world compete. In Malvern band we have the men, and in Mr. Harry Shugg we have the man. Yours, etc., J. STURT ANDERSON
(Anderson, 1920)
This letter by Mr. Anderson was published in the Prahran Telegraph newspaper on the 6th of November 1920, two weeks after the afore mentioned Malvern Tramways Band won the A Grade Section at the Royal South Street contests. His letter is telling for many reasons, namely, for the high-praise language that he used, and because he advocates for the band to travel to the United Kingdom (U.K.). This is for a band that in 1920 is only nine years old, yet up to this point, had a contesting record which was enviable in the Australian band movement. What Mr. Anderson probably foresaw, but could not have known at the time, was that Malvern Tramways Band was going to get better in the very near future…and they did.
As will be seen throughout this post, there is an ongoing tussle between hype and reality, and expectation could probably be mixed into this as well. On one hand, we have a highly regarded brass band that is lauded at every opportunity for their playing. With this reputation, commentators and others talk up the prospect of sending the MTB to the U.K. compete and try to predict how well they will do when they get there. This is the hype. One reality, as we will find, was that the MTB was that good. However, the other reality is that travel overseas for any ensemble was expensive, as we saw in a previous post.
This is the story of why the MTB never travelled the U.K. within a time frame that spans the best part of a decade from 1920-1927. In this post we will unpick the reputation of the MTB in the 1910s and 1920s, their contesting record, and the inter-related stories of other bands that were also trying to travel. We will also see where the travel plans took them and the talk about the personalities that were involved. This is a band that gained an amount of support for their endeavours and plans. Alas that it never came to be.
The Malvern Tramways Band: building a reputation:

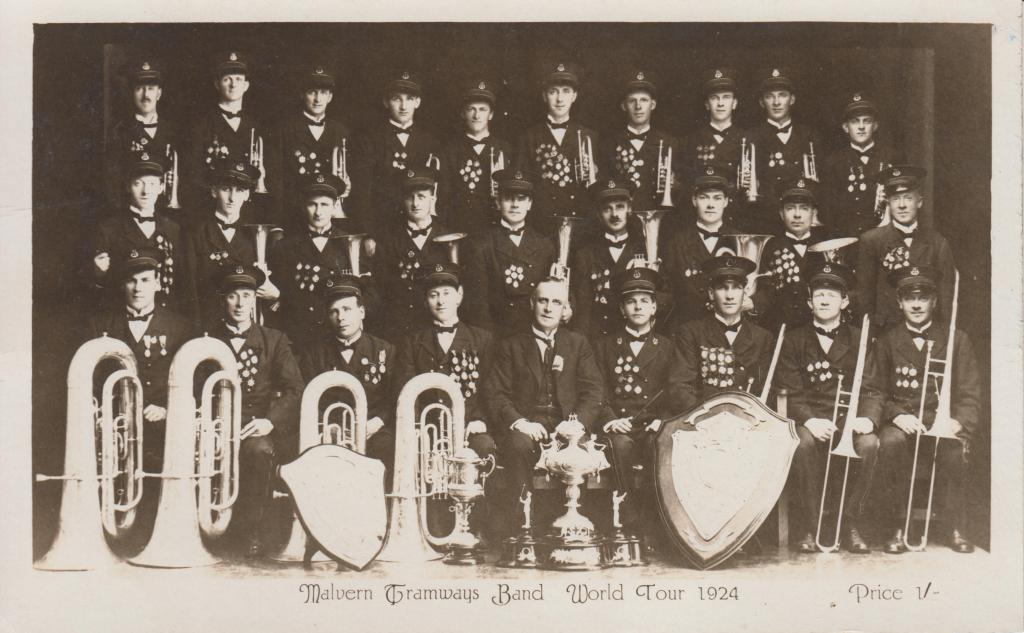
(Source: Jeremy de Korte Collection)
Above is the contesting record of the Malvern Tramways Band up to 1922 which was printed on the back of a souvenir postcard published in 1924. This record established the reputation of the MTB as one of the finest brass bands in Australia at the time. When considering the range of measures the MTB had in their favour during these years, including fine musicians and conductors, as well as a very active committee and the industry that supported the band, the advantages immediately become obvious.
Just looking at the conductors by themselves up to 1922, the MTB had the very best. From their inception in 1911 to 1914, they were conducted by Mr. William Ryder of Besses o’ th’ Barn Band fame, a musician who was detailed in a previous post (de Korte, 2018b). He led the band to its first contest win in 1912 in C grade after only thirteen practices where they surprised everyone – the Victorian Bands’ Association promptly promoted the band to B grade (Zealley & Ord Hume, 1926).

The second conductor of the MTB was the great Mr. Robert McAnally who took over for a short stint up until 1915 when Mr. Harry Shugg started a very long association with the band that lasted thirty-one years (Lawson-Black, 2010). These three famous musicians provided a foundation of musicianship and conducting for the band that set the MTB on a path to greatness in the early years of the band. By the time Mr. Shugg started at Malvern, he had already several successes at South Street with the Geelong Harbour Trust Band (Quickstep, 1920). Out of the three of these men it was Mr. Shugg that had the greatest impact and it is during his tenure that the MTB was primed to travel to the U.K.

The Malvern Tramways Band at South Street:
Thanks to visits from some of the top bands in the world at the time, namely the Besses o’ th’ Barn Band and adjudicators from the U.K. from the early 1900s and beyond, the Australian band movement underwent a rapid rise in standards (de Korte, 2021). The Malvern Tramways Band, although having started during this rise, was also a beneficiary with the mentioned conductors doing their part to take Malvern to new heights. In addition, the South Street band sections, having been added to the eisteddfod programme in 1900, were regarded as the premier band competitions in Australia (Greaves, 1996).
If we drill down into the MTB contest results a bit deeper, it is the last three on the postcard that provide the most interest, a hattrick of wins at the Ballarat South Street Eisteddfod in 1920, 1921, & 1922 (Royal South Street Society, 1920, 1921, 1922). Of course, their earlier contest results were important in the development of the band. However, in terms of context, the MTB achieved a string of results that cemented their status, and prompted the speculation and commentary of when, not if, they would travel to the U.K.
The MTB was not only renowned for their contest successes. They were an extremely hardworking band that endeared themselves to the local community through their charity work, community singing events, performances, and parades (Lawson-Black, 2010). And while they were nominally a band strongly supported by the Malvern tram depot, they also were strongly supported by the Malvern City Council who considered them as the council band (de Korte, 2022).
Rivalry:
By 1922, there was no shortage of bands trying to bump Malvern off its status as the champion band of Australia. As Zealley & Ord Hume (1926) noted in the chapter on Malvern Tramways in their book ‘Famous Bands of the British Empire : Brief Historical Records of the recognized leading Military Bands and Brass Bands in the Empire’,
There have been 7 A grade contests in Victoria since Malvern has been an A grade Band (1915-1921) : Malvern was eligible to enter five of these and received 1st place on each occasion.”
(p. 60)
There were some Victorian A grade bands that were considered the main rivals of Malvern in competition namely Collingwood Citizens’ – they drew with Malvern at the 1915 South Street Eisteddfod – Hawthorn City, City of Ballarat, and St. Augustine’s Orphanage Band (Royal South Street Society, 1915, 1920, 1921, 1922). And then there were some interstate rivals including Newtown, South Sydney, Ipswich, and perhaps it’s greatest rival of the time, the Newcastle Steel Works Band (Greaves, 2005; Royal South Street Society, 1920, 1921, 1922). Although the Newcastle Steel Works Band only entered the South Street contests twice in these years, 1921 & 1922, they came second to Malvern both times (Greaves, 2005). However, unlike Malvern, the Newcastle Steel Works Band, then conducted by the great Albert Baile, did end up travelling to the U.K. in 1924, and won or placed in every contest that they entered (Greaves, 2005; Greaves & Earl, 2001).
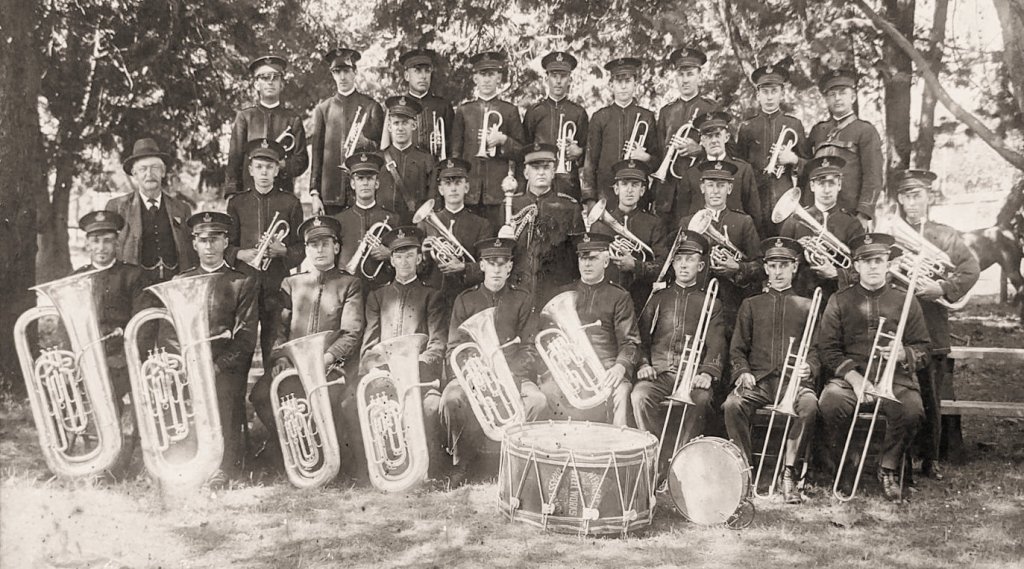

What if the MTB had made it to the U.K. and competed in their famed brass band contests? Some commentators felt they were a much better band than Newcastle…
The first attempt: “To Seek Fresh Fame in England”:

Do not believe the hype. But no one told the newspapers and other commentators of the day. After each of the three wins at South Street, the legendary status of the MTB only grew bigger. So did the garnering of support to send the band to the U.K.
The letter from Mr. J. Stuart Anderson at the head of this post could be considered the start of the commentary and hype. Sure enough, by early 1921, an announcement was made by the MTB that they would seek to go to the U.K. in 1924, news that surprised no one and was announced in newspapers up and down the country. The article below published by the Northern Star newspaper of Lismore, N.S.W. in February 1921 being one example.

In October 1922 the MTB achieved the hattrick at South Street and once again carried off the Boosey Shield (Royal South Street Society, 1922). The MTB and its conductor Mr. Harry Shugg drew widespread praise for their win and the adjudicator, Mr. Christopher Smith, from Adelaide and a former conductor of the Besses o’ th’ Barn Band had this to say about the MTB. Two Victorian newspapers, The Herald and The Prahran Telegraph, published his comments on the band and the musical genius of Mr. Shugg.
Malvern Tramways Band is such a cultured musical combination that it would capture English audiences by its playing. It would do so by sheer merit.
[…]
The successful conductor is a puzzle. To me he is only a boy, and I wonder where he gets such beautiful effects. He is a genius in the middle of a band, seeming to be ever striving after the unattainable, and getting nearer to it all the time. Let Melbourne send the boy and his band to London, and Londoners will take them to its collective bosom, and perhaps never allow them to leave.
(Smith in “Malvern Tramways Band.,” 1922)
The articles from the newspapers, while helpful, could only promote so much news about the band from their own correspondents. From the MTB’s perspective, driven as they were to get to the U.K. by 1924, they needed someone who was a networker and promoter, as well as being a musician, to help them manage the tour arrangements. That person was Mr. Gibson Young, and he got stuck straight into the job as tour manager.
Mr. Gibson Young, musical influencer:
The MTB won the 1922 South Street A Grade section in October of that year, by December, an announcement was made that Mr. Gibson Young would be the “business manager and organiser of the world tour” (“A BAND ABROAD,” 1922). In Mr. Young, the MTB could not have made a better choice of tour manager.
Mr. Young was not unknown to the musical circles of Melbourne. He mainly known as an accomplished singer and music critic, and claimed to have been the first person to introduce community singing events to Melbourne in 1919 – events that soon attracted huge numbers of people (“GIBSON YOUNG,” 1936). His ability to promote and network, and his eloquent writing, was evident as Mr. Young sought to talk up the proposed tour of the MTB to the U.K. His description of a MTB rehearsal which opens an article published by The Herald newspaper on the 4th of December 1922, shows readers the inner workings of this band.
High up near the roof, and overlooking a sea of tramcars, is an employee lunch room at the Malvern Tramway sheds. Here a human dynamo induces into one circuit, or magnetic field of action, 30 players who make up the personnel of the Malvern Tramways Band – the champion brass band of Australia.
(Young, 1922)
Having introduced the band, Mr. Young goes on to write about the influence of Mr. Harry Shugg and how he shapes the sounds in rehearsal. However, in the last paragraph of the article, attention turns to the upcoming tour and the feelings of the band members. It is obvious that Mr. Young has possibly attended his first real rehearsal of the MTB and is astute in his observations. He may not understand the band yet, but he does understand musical finesse and can see what the MTB is striving to achieve.
And then these coatless musicians become a round table of smokers, discussing the all-absorbing topic – the band’s world tour to begin in March 1924. For 12 years the members of this band have given unsparingly, and without reward, the energy of enthusiasm which is said to be able to move mountains, and at least it seems as though this self-sacrifice is to be rewarded. No need to remind these men that they must compete with the world’s best, and that an Australian band may not necessarily be successful at Manchester or the Crystal Palace. For the next 15 months the men will have little else in their minds, and Harry Shugg will leave nothing to chance. The moral of this band is good now, Mr. Shugg expects it to be almost perfect in March, 1924.
(Young, 1922)
Up until September 1923, Mr. Young worked ceaselessly to promote the band and the tour by regularly penning articles and letters in newspapers, networking with politicians and community members, visiting various other states, and trying to secure more funding. Interestingly, he also uses his prowess in promoting community singing as a funding source for the band by having the band provide the accompanying music for community singing events (“MALVERN BAND CONCERTS,” 1923). This initiative started in January 1923 and collections were taken at each concert in Malvern and St. Kilda to benefit the touring fund.
There is no doubting the combination of community singing with the band was hugely successful. Mr. Young writes in a letter to The Herald newspaper on the 17th of January that 8,000 people had attended the most recent event at the Malvern Cricket Ground (Young, 1923h). Booklets of the songs were also produced and sold to attendees as another form of funding for the tour (Malvern Tramways Band, 1923). One page of this booklet is devoted to a letter written by Mr. Young inviting interested parties to a public meeting in May and subscribing to shares in a company set up to fund the tour (Young, 1923b). Mr. Young is quite honest in this letter as he suggests up to “£20,000” will be needed to fund the tour (Young, 1923b, p. 24). But he also tries to talk up the potential earnings of “£40,000” from the tour which he expects will be earned from 200 concerts across Australia, New Zealand, Great Britain, and other countries (Young, 1923b, p. 24).

Community singing : St. Kilda Esplanade every Wednesday evening : words of songs & program, 1923 (Source: National Library Australia: nla.obj-52777212)
Mr. Young worked to solicit money from other sources while promoting the tour. In early April 1923 he was adjudicating in Launceston, Tasmania, and being the opportunist organises a concert with the Launceston City Band accompanying a community singing event with the money going towards the MTB tour (“MALVERN TRAMWAY BAND,” 1923). In May of 1923 we see that Mr. Young has approached the Federal Government for funding (“AN ENGLISH TOUR.,” 1923).

In some ways, Mr. Young provides the best commentary of all as he draws everyone into the potential of this tour. Occasionally, and perhaps naively, he invites controversy in his articles and letters. One article written in February 1923 where he takes aim at the Redfern Band of Sydney is an example of this (Young, 1923f). Later that year in May, Mr. Young pens another letter where he outlines a conversation he had with Mr. W. Partington, then conductor of the South Sydney Band of Redfern about the touring plans of the MTB (Young, 1923g). At the time, Mr. Partington is trying to raise his own all-Australian band, the Australian Imperial Band (AIB), to go to the U.K. in 1924 (de Korte, 2019a).
Three more letters were written to The Age, The Argus, and The Prahran Telegraph newspapers in April 1923 by Mr. Young as he seeks to dispel a rumour that the bandsmen are taking their wives using the band funding (Young, 1923c, 1923d, 1923e). One of Mr. Young’s more interesting letters was written in June 1923, just before the public meeting on June 14th where he addressed the composition of the touring party. Basically, he points out that some of the other attempts at touring parties were bands made up of bandmasters, unlike the MTB which has one band conductor and a band made up of very fine musicians (Young, 1923a). He is firm, but polite in this letter, especially in the first paragraph.
Sir. – Your correspondent, Mr Herbert Eden, is apparently acquainted with the full history of the attempts which have been made to send an all-Australian band abroad. He also realises how essential it is that any band that leaves Australia should have official status as a winner of championships, and that it should not merely be a combination of bandmasters filled with the wanderlust.
(Young, 1923a)
This is where Mr. Young leaves this story as he was busy organising the public meeting, but he will be back as this story is not quite done with him yet.
Some funding: then a reality check:

By June 1923 the organising of the tour was well-underway with Mr. Young at the helm of the business side of things, along with the president and committee of the MTB. There was some money coming in, and important figures had been engaged to lend support. Now, it was time to form the company to handle the touring money and for the public to buy into the tour.
On the 14th of June the MTB held a public meeting at the Malvern Town Hall where interested parties were invited to buy shares in the band company. By all accounts it was a grand affair with many councillors, dignitaries, members of the public, and three other metropolitan brass bands, Brunswick, Caulfield, and Hawthorn who teamed up with Malvern to present a recital on the front steps of the hall before proceedings commenced (“TOUR-SCHEME LAUNCHED,” 1923).
The challenge from the English band authorities had been accepted (“MALVERN BAND,” 1923a). To the keen observer, however, reality was obviously beginning to hit. The meeting was only attended by two-hundred interested parties and by the end of the night, only £2,000 had been raised (“TOUR-SCHEME LAUNCHED,” 1923). When Malvern Councillor Wettenhall “said that it was estimated that £10,000 would need to be subscribed before the band commenced the tour” (“MALVERN BAND,” 1923a), he was highlighting a certain reality of the situation.
Tour abandoned:

By the end of September 1923, reports that the Malvern Tramways Band had abandoned their tour began surfacing, as the article above shows (“MALVERN BAND,” 1923b). By early October, it had been confirmed. Disappointment was an understatement as it was realised that many factors were against raising more funds. The band said that it was not due to the administration being faulty, and one could readily believe that given the management of the MTB and nous of Mr. Gibson Young (“MALVERN BAND,” 1923b). The decision to abandon the tour was mainly due to an almost complete lack of funds at a time when they needed them most. As part of an article published in the Geelong Advertiser lamented,
The paltry response by the public generally shows how little even a great musical combination like the Malvern Band, with its brilliant record of successes, counts within the public when it comes to a practical point.
(“WORLD TOUR DROPPED,” 1923)
It was probably fortunate the band abandoned the tour when it did considering the futility of trying to raise around £7,500 in such a short time frame (“WORLD TOUR DROPPED,” 1923). Also, there were factors overseas that were against them, mainly economic conditions (“MALVERN BAND WORLD TOUR.,” 1923).
The aftermath:
From viewing the newspaper articles of the day, perhaps the Prahran Telegraph newspaper offered the most pragmatic response to the abandonment of the tour, laced with a bit of local self-interest.
That the Malvern Tramway Band would have gained world laurels those most competent to judge have little or no doubt about it. The world’s loss is our district’s gain, and not a few, who made it a habit to attend the Malvern Band recitals, will be pleased to know that they will be still able to listen this summer to the exquisite playing of the Malvern Tramways Band
(“MALVERN BAND WORLD TOUR.,” 1923)
Oddly, perhaps the MTB still felt there was some kind of chance to go to the U.K. to compete, even though the tour had been officially abandoned, perhaps in administration but not in mind. In early April 1924, letters were published in all the major Victorian newspapers written by Mr. Frank Garson, then President of the MTB. It seems the MTB were a bit put out at the thought that the Australian Imperial Band might make it to the U.K. instead of the MTB.
Sir, – I am instructed by the committee of the Malvern Tramways Band to ask, through this column of your valuable paper, for the public support to send this band to compete at Belview Manchester, for the brass band championship of the British Exhibition in 1924. This band endeavoured to raise funds for a company, but was unable to get the necessary capital. I notice that the Lord Mayor of Melbourne (Cr. W. Brunton) has convened a meeting of citizens, to be held in the Melbourne Town Hall on Thursday, April 3, to consider the sending of an Australasian Imperial Band to the Empire Exhibition.
(Garson, 1924)
After outlining the credentials of the MTB (which most people were probably aware of), Mr. Garson did not ask for that much!
We have a complete set of uniforms and instruments, and can leave in a month’s time. All that will be necessary if for 150 residents of Victorian to contribute £50 each. Any surplus will be returned to the contributors. In the event of the band not going all money will be returned. Trusting this appeal will meet with success. – Yours, etc.
(Garson, 1924)
There is no indication that this appeal for late money was in any way successful.
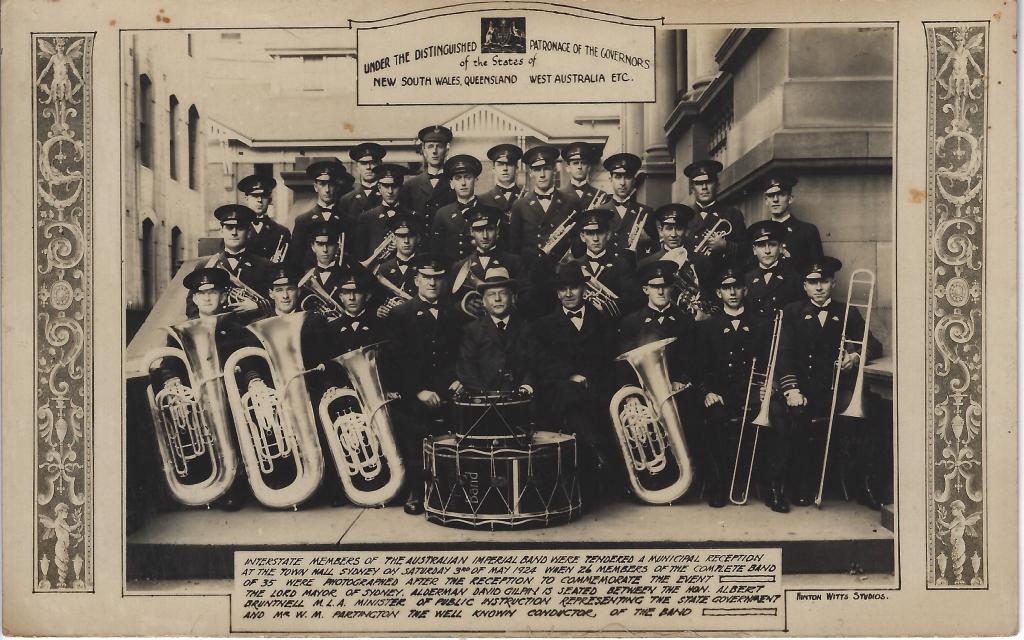

For the rest of the Australian band movement, the desire to go to the U.K. and compete still resonated in a couple of bands, and the hole left by Malvern’s absence was to be filled by another Australian band. The two bands in the running were the Australian Imperial Band conducted by Mr. W. Partington and the Newcastle Steel Works Band conducted by Mr. Albert Baile.
Briefly, the Australian Imperial Band was an ensemble made up of many fine brass musicians from around Australia and they proceeded to go on a grand tour around Australia to raise funds, and which no doubt cost them money. However, when they reached Perth and were just about to sail to the U.K, the funds had run out – they needed more funds, but the money was not forthcoming (Mitchell, 1924). This is one band that had not heeded the lesson from the MTB’s failed attempt at travelling to the U.K.

Then there were the exploits of the Newcastle Steel Works Band, which has previously been mentioned in this post. They had been quietly preparing for their own tour and when the chance to go came up, they took it (Greaves, 2005).
As for Mr. Gibson Young, his appointment with the MTB ended with the abandonment of the tour, so was free to do as he wanted, but did not let his experiences with a brass band go to waste. Ever the musician, he had kept up numerous activities while associated with the MTB. And as we found in a previous post, one of these appointments was directing the brass band and community singing at Pentridge Prison, which he left at the end of September to travel to the U.K. (de Korte, 2023; “GAOL MUSIC,” 1923). He was spotted in Perth in November before sailing for the U.K., where his photo and article published by the Sunday Times newspaper mentioned his new appointment.

In January 1924 it was announced that Mr. Gibson Young had contracted an Imperial Band from Australia to play at the Wembley Exhibition for eight weeks (“VICTORIAN BAND,” 1924). It was not hard to work out which band had been contracted (and it was not Victorian), but we know what happened to the AIB and its plans for this tour. He also put on his other hat as a music critic early in his next stay in the U.K. and wrote a very useful critique of the 1924 contest at Crystal Palace where the Newcastle Steel Works Band came third. In this article published by The News newspaper in Adelaide in November 1924, he observed some distinct differences between South Street and the U.K. contests.
Unlike South street, the adjudicators allot no marks and make no remarks. Presumably they judge by a combined process of impression and elimination, in my opinion, a difficult, dangerous, and unsatisfactory method. Too much strain is placed on the judge’s psychology, and too much depends on the playing position of the winning band in the draw.
(Young, 1924)
And interestingly, he had this to say about final adjudication.
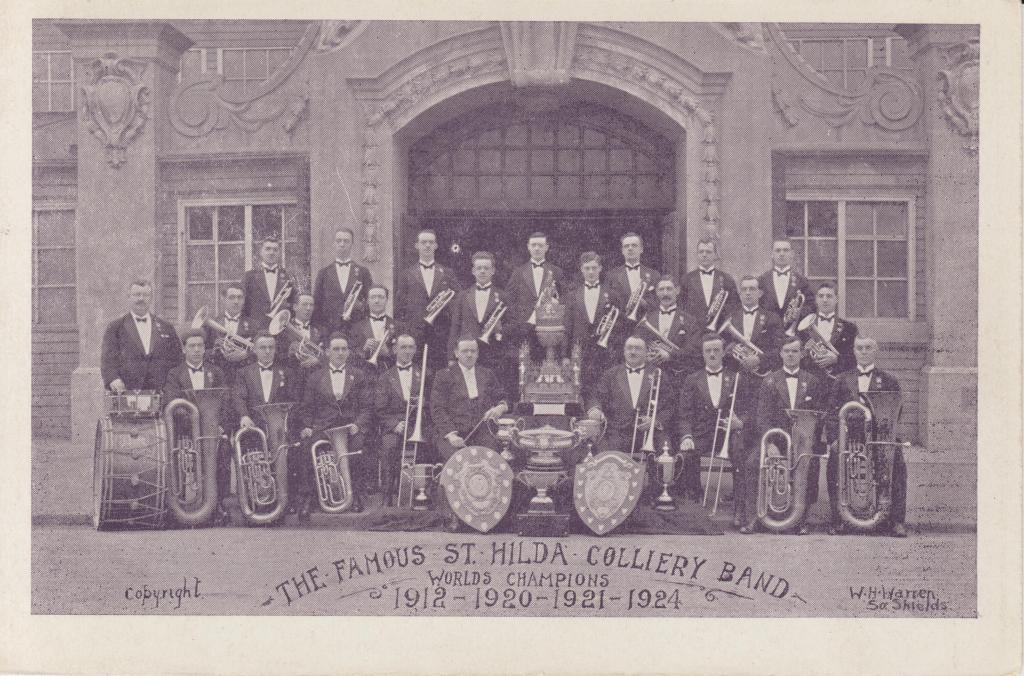
Out of the 17 competing bands, not more than ten appealed to me as essentially A grade. There are at least four Australian bands, not counting the Australian Imperial, which I have not heard, which could have defeated all the starters save one, the winner – St. Hilda’s Colliery Band. In my opinion and judging by the type of performance favoured by the judges, brilliant tone and a technically flawless performance, the Malvern Tramways Band would have won the contest given equal rehearsal opportunities with St. Hilda’s. The first three bands were St. Hilda’s, Black Dyke, and Newcastle (New South Wales) Steel Works in that order.
[…]
Some members of the Newcastle Band created mild amusement and some criticism by calmly and nonchalantly stripping off their tunics on the stage and playing in their shirtsleeves. This was not a gesture of defiance, but a natural desire to be comfortable.”
(Young, 1924)

After a long absence from Australia, Mr. Young came back from England in April 1936 but by November he had sadly passed away at the relatively young middle-age of 48 (“GIBSON YOUNG,” 1936; “Mr. ERNEST GIBSON YOUNG.,” 1936).
This ends the story of the first tour plan with all the hype, and reality that led up to the tour being abandoned. But the Malvern Tramways Band did not rest, there were other things to do, and dreams do not always fade.
A side note: the 1925 consolation tour of New Zealand:

If there was one lesson that the MTB learned from their failed attempt to get to the U.K., it was to have a proactive and varied fundraising strategy if they were to go on international trips. With this in mind, in August 1924, the MTB made the decision to go to New Zealand in February 1925 to compete at the New Zealand National Band Championships, a trip that would probably be cheaper than a jaunt to England (“MALVERN TRAMWAYS BAND,” 1924). At this time, the band sections of the South Street Eisteddfod were not run from 1924-1932 and this left a gap in the competition calendar. While they could enter, and did enter, many other competitions around Australia during this time, the New Zealand trip offered them a different opportunity Once again, aspects of this tour have been documented in a previous post so the details of the fundraising effort have been noted here (de Korte, 2019b).
One cannot fault the MTB for their innovative and impressive fundraising efforts to get the band to New Zealand, and in November 1924, this fundraising effort was on full show. There were two major events in November that the MTB organised. The first event was a Massed Bands recital at the Melbourne Cricket Ground (M.C.G.) which was held in front of a crowd of 15,000 people (“MASSED BANDS PLAYED,” 1924). All members of the crowd were admitted by silver coin, and the MTB invited another eleven suburban bands to help them – as with any band event at the M.C.G., bands marched from Princes Bridge to the ground (“MASSED BANDS PLAYED,” 1924).
From the various suburbs 11 bands rallied, assembling at Prince’s Bridge and marching to the ground.
They were the Preston Citizens’ Band, Williamstown City Band, Caulfield District, Malvern City Band, Carlton Citizens’ Band, Footscray City Brass Band, Malvern Drum and Bugle Band, 32nd Battalion Band, Yarraville and Williamstown Naval Drum and Bugle Band, Collingwood Junior Brass Band, and the Burnley Band.”
(“MASSED BANDS PLAYED,” 1924)
This was quite the line-up of bands, including some that would not normally get to participate in this kind of event. For some, like the Burnley Brass Band, it was a very special experience and the fact that the great MTB invited them made it even more special (“Burnley Brass Band.,” 1924).
Two weeks later the MTB held a carnival at the Malvern Cricket Ground and it was not a small affair It comprised of a sports carnival involving thirty athletic clubs, a Highland Dancing competition, and a dance at the Malvern Town hall (“MALVERN BAND CARNIVAL.,” 1924). And just to top things off, for the musical entertainment there were five brass bands and three highland bands (“MALVERN BAND CARNIVAL.,” 1924).
Gaining all the funding that they needed, the MTB started their six week tour of New Zealand on the 4th of February by sailing for Invercargill on the South Island (“MALVERN TRAMWAYS BAND,” 1925a). And as they were nominally a tramways band, the NZ authorities gave them free travel on all NZ trams and reduced fares on the trains as the travelled up from Invercargill to Auckland, playing recitals in every locality that they visited (“MALVERN TRAMWAYS BAND,” 1925a; “MALVERN TRAMWAYS BAND,” 1925b).
Perhaps the end results of the competition were a foregone conclusion as the MTB dominated proceedings in Auckland. The New Zealand bands were no match for the MTB and the championship points reflected this – ten points separated the MTB from the next band in the A Grade test section (“MALVERN WIN A GRADE TEST,” 1925; Newcomb, 1980).

Ngā Pātaka Kōrero o Tâmaki Makaurau / Auckland Libraries Heritage Collections: AWNS-19250305-46-1)
Obviously, the win in New Zealand was impressive and only served to boost the reputation of the MTB. However, later in 1925, hype started building again and speculation grew that the MTB might again try to get to the U.K. to compete.
1926: The year they tried again:
There are several very fine bands in Australia, and I have heard some of the best of them, including the Malvern Tramways Band,” says Mr J Ord Hume, the well-known band adjudicator, in an interview published in the English Band News on his return to England from his visit to Ballarat.
“Melbourne has the finest all-round bands. There are also some very find bands in New South Wales and Western Australia,…Again, in my opinion, there are several much better bands than the Newcastle Steel Works Band (which won important contest in England), and the only thing required by all Australian bands in better and more finished tuition.”
(Ord Hume in “AUSTRALIAN BANDS,” 1925
James Ord Hume was not the only eminent band personage to have added his thoughts about the MTB, there were lots of others. What set these comments, and others apart, was the thoughts that the MTB was an infinitely better band than Newcastle Steel Works (“MALVERN TRAMWAYS BAND.,” 1926a). A flurry of articles was published in newspapers throughout April and May 1926 that reported on another planned trip by Malvern to compete in the U.K. in 1927. Much was made of the fact that the MTB was made up of working men and that the band needed more support from the public, as Mr. R. T. Patterson, President of the Management Committee explained in an interview.
We play all day on Sunday, practicing in the morning, performing at the Wattletree road park in the afternoon, and at the Central Gardens in Malvern, in the evening. The Tramways Board gives us a small subsidy for the afternoon performance, and the Malvern Council this year gave us £100 for playing at Central Gardens. But, although we often have 2000 people at these performances, collections yield very little.
(Patterson in “APPEAL FOR BAND,” 1926)
However, a headline in an article published in April 1926 by The Sun News-Pictorial newspaper might as well have been the most realistic about this latest effort, as can be viewed in the article below.

At a special performance by the MTB and assisted by the Geelong Municipal Band at Central Park, Malvern, the Mayor of Malvern officially launched the campaign to send the MTB abroad (“MALVERN TRAMWAYS BAND.,” 1926b). One of the dignitaries was a Mr. J. Venn of London who was representing the brass bands of the U.K.
Mr. Venn, speaking on behalf of the bands of Great Britain, said the British bandsmen would welcome the Malvern Tramways Band with open arms. They preferred a regular band much before a composite band drawn from all parts of a State.
(“MALVERN TRAMWAYS BAND.,” 1926b)
But as could be predicted, this second attempt by the MTB to get to the U.K. also came to nought, and the reasons why would probably be financial. Although, unlike the first tour when the abandonment was widely reported on, there was almost nothing in the papers in this instance. The last we hear of this tour is an article from April 1927 published in the Geelong Advertiser newspaper where, according to sources, the bandsmen of New Zealand give their best wishes to Malvern on their tour.” (“The Malvern Band,” 1927).
A tour which did not happen.
Conclusion:
The Malvern Tramways Band tried their best to answer the hype and expectations thrust upon them by an eager community who wanted the MTB to take their playing to the U.K., and win. There was no doubting that the MTB deserved all the accolades during these years as they were that good. There was probably no doubt that they would do very well in the U.K., as the commentators and adjudicators suggested. However, the pervasive reality around finances and funding was always going to surround their two attempts. As for an overseas trip, New Zealand would have to do.
The rhetorical what if question as to how well the MTB would do in the U.K. will probably be debated for as long as the history lasts. The MTB are legends in the Australian band movement, but in this year, a full century after they should have gone to the U.K., the debate still comes up. Band historians can continue this discussion when time allows.
Hype versus reality. An age-old tussle that never goes away.
References:
Anderson, J. S. (1920, 06 November). AUSTRALIA’S CHAMPION BAND : Malvern Tramways Band. Prahran Telegraph (Vic. : 1889 – 1930), 5. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article165153504
APPEAL FOR BAND : Champions Want to Tour Britain. (1926, 06 April). Herald (Melbourne, Vic. : 1861 – 1954), 4. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article243591118
Auckland Weekly News. (1925). Australian band’s sweeping success : Malvern Tramways (Melbourne), Winners of all the A Grade Shields and the McLeod Cup. In Auckland Weekly News (AWNS-19250305-46-01 ed., pp. 46). Auckland, N.Z. https://kura.aucklandlibraries.govt.nz/digital/collection/photos/id/244635/rec/1: Ngā Pātaka Kōrero o Tâmaki Makaurau / Auckland Libraries Heritage Collections.
AUSTRALIAN BANDS : Mr Ord Hume Likes Malvern Tramways. (1925, 11 June). Herald (Melbourne, Vic. : 1861 – 1954), 25. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article244047022
A BAND ABROAD : Malvern Players Tour : Manager Appointed. (1922, 01 December). Herald (Melbourne, Vic. : 1861 – 1954), 1. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article246675723
BAND OF WORKERS : Music Strong, Finance Weak. (1926, 07 April). Sun News-Pictorial (Melbourne, Vic. : 1922 – 1954; 1956), 5. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article274798889
BAND OFF TO ENGLAND. (1921, 14 February). Northern Star (Lismore, NSW : 1876 – 1954), 3. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article93115301
Burnley Brass Band. (1924, 11 October). Richmond Guardian (Vic. : 1884 – 1885; 1894 – 1897; 1900 – 1930), 2. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article265748535
de Korte, J. D. (2018a, 14 October). International band tours of the early 1900’s: bringing music to Australia. Band Blasts from the Past: Anecdotes, Stories and Personalities. https://bandblastsfromthepast.blog/2018/10/14/_international-band-tours-of-the-early-1900s-bringing-music-to-australia/
de Korte, J. D. (2018b, 02 March). William Ryder: The first conductor of the Prahran & Malvern Tramways Employees Band. Band Blasts from the Past: Anecdotes, Stories and Personalities. https://bandblastsfromthepast.blog/2018/03/02/william-ryder-the-first-conductor-of-the-prahran-malvern-tramways-employees-band/
de Korte, J. D. (2019a, 24 March). Names and status: the rare National and State bands. Band Blasts from the Past: Anecdotes, Stories and Personalities. https://bandblastsfromthepast.blog/2019/03/24/names-and-status-the-rare-national-and-state-bands/
de Korte, J. D. (2019b, 03 August). Trans-Tasman connections: the lure of competition and performance. Part Two – Australian Bands in New Zealand. Band Blasts from the Past: Anecdotes, Stories and Personalities. https://bandblastsfromthepast.blog/2019/08/03/trans-tasman-connections-the-lure-of-competition-and-performance-part-two-australian-bands-in-new-zealand/
de Korte, J. D. (2021, 16 February). Influences from Britain: James Ord Hume and “The Besses Effect”. Band Blasts from the Past: Anecdotes, Stories and Personalities. https://bandblastsfromthepast.blog/2021/02/16/influences-from-britain-james-ord-hume-and-the-besses-effect/
de Korte, J. D. (2022, 31 July). A band, council, correspondence, and financial records: a case study of the Malvern City Band. Band Blasts from the Past: Anecdotes, Stories and Personalities. https://bandblastsfromthepast.blog/2022/07/31/a-band-a-council-correspondence-and-financial-records-a-case-study-of-the-malvern-city-band/
de Korte, J. D. (2023, 23 April). A pastime with a purpose: band music in our institutions and the fourth prison band in the world. Band Blasts from the Past: Anecdotes, Stories and Personalities. https://bandblastsfromthepast.blog/2023/04/23/a-pastime-with-a-purpose-band-music-in-our-institutions-and-the-fourth-prison-band-in-the-world/
AN ENGLISH TOUR : MALVERN TRAMWAY BAND. (1923, 17 May). World (Hobart, Tas. : 1918 – 1924), 5. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article190297002
GAOL MUSIC. (1923, 22 September). Mirror (Perth, WA : 1921 – 1956), 2. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article77760324
Garson, F. (1924, 04 April). MALVERN TRAMWAYS BAND : TO THE EDITOR. Prahran Telegraph (Vic. : 1889 – 1930), 5. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article165094667
GIBSON YOUNG : Pioneer of Community Singing : Returns After Absence of 13 Years. (1936, 28 April). Telegraph (Brisbane, Qld. : 1872 – 1947), 6. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article183389164
Greaves, J. (1996). The Great Bands of Australia [booklet] [2 sound discs (CD) : digital ; 4 3/4 in. + 1 booklet]. Sydney, N.S.W., Sound Heritage Association Ltd. https://catalogue.nla.gov.au/catalog/2372005
Greaves, J. (2005). A musical mission of Empire : the story of the Australian Newcastle Steelworks Band. Peters 4 Printing. https://catalogue.nla.gov.au/catalog/3640204
Greaves, J., & Earl, C. (2001). Albert Baile : August 10 1882 – March 14 1961. In Legends in brass : Australian brass band achievers of the 20th century (pp. 11-12). Muso’s Media. https://catalogue.nla.gov.au/catalog/1522216
Lawson-Black, P. (2010). Bold as brass : the story of Stonnington City Brass then and now. Pat Lawson Black, Stonnington City Brass. https://find.slv.vic.gov.au/permalink/61SLV_INST/1sev8ar/alma9921636883607636
The Malvern Band. (1927, 04 April). Geelong Advertiser (Vic. : 1859 – 1929), 4. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article232380492
MALVERN BAND : ENGLISH CHALLENGE ACCEPTED. (1923, 16 June). Geelong Advertiser (Vic. : 1859 – 1929), 5. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article166013099
MALVERN BAND : Proposed World Tour : May be Abandoned. (1923, 28 September). Sun News-Pictorial (Melbourne, Vic. : 1922 – 1954; 1956), 8. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article274210227
MALVERN BAND CARNIVAL. (1924, 15 November). Argus (Melbourne, Vic. : 1848 – 1957), 22. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article2069105
MALVERN BAND CONCERTS : Community Singing on Sunday Nights. (1923, 06 January). Herald (Melbourne, Vic. : 1861 – 1954), 5. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article246670527
MALVERN BAND WORLD TOUR. (1923, 05 October). Prahran Telegraph (Vic. : 1889 – 1930), 6. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article165100079
MALVERN TRAMWAY BAND : Acclaimed at Ballarat : The Champion Band. (1922, 03 November). Prahran Telegraph (Vic. : 1889 – 1930), 7. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article165129241
MALVERN TRAMWAY BAND : PROPOSED WORLD TOUR : ASSISTANCE FROM LAUNCESTON. (1923, 05 April). Daily Telegraph (Launceston, Tas. : 1883 – 1928), 2. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article153414987
MALVERN TRAMWAYS BAND. (1924, 06 August). Herald (Melbourne, Vic. : 1861 – 1954), 5. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article243887504
MALVERN TRAMWAYS BAND. (1925a, 20 January). Herald (Melbourne, Vic. : 1861 – 1954), 16. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article243874312
Malvern Tramways Band. (1923). Community singing : St. Kilda Esplanade every Wednesday evening : words of songs & program. Malvern Tramways Band. http://nla.gov.au/nla.obj-52777212
MALVERN TRAMWAYS BAND : Concerts in the Domain. (1925b, 20 February). New Zealand Herald. https://paperspast.natlib.govt.nz/newspapers/NZH19250220.2.132
MALVERN TRAMWAYS BAND : High Praise From English Critic. (1926a, 08 May). Argus (Melbourne, Vic. : 1848 – 1957), 22. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article3780673
MALVERN TRAMWAYS BAND : Projected Tour Abroad. (1926b, 24 November). Age (Melbourne, Vic. : 1854 – 1954), 12. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article202212517
MALVERN WIN A GRADE TEST : PORT NICHOLSON SECURE FIFTH PLACE. (1925, 27 February). Evening Post. https://paperspast.natlib.govt.nz/newspapers/EP19250227.2.83.1
MASSED BANDS PLAYED : 15,000 Listened : FUNDS FOR MALVERN. (1924, 03 November). Sun News-Pictorial (Melbourne, Vic. : 1922 – 1954; 1956), 11. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article274432031
Minton Witts Studios. (1924). Australian Imperial Band in Sydney (Conducted by: Mr W. M. Partington) [Postcard]. Minton Witts Studios, Sydney, N.S.W.
Mitchell, E. L. (1924, 09 August). “WE WANT SOME MONEY-GIVE US SOME, DO!”. Mirror (Perth, WA : 1921 – 1956), 1. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article76437154
Mr. ERNEST GIBSON YOUNG. (1936, 02 November). Age (Melbourne, Vic. : 1854 – 1954), 12. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article205944529
Muntz, D. L. (1924). Malvern Tramways Band World Tour 1924 [Postcard]. Muntz Studio Pty. Ltd., Malvern, Victoria.
Muntz Studio. (1922, 28 September). TO SEEK FRESH FAME IN ENGLAND : Malvern Tramways Band and its Young Conductor. Herald (Melbourne, Vic. : 1861 – 1954), 15. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article243779263
Newcastle Steel Works Band. (1922). [Photograph]. [phot20975]. The Internet Bandsman Everything Within, Vintage Brass Band Pictures – Australia. http://www.ibew.org.uk/vbbp-oz.html
Newcomb, S. P. (1980). Challenging brass : 100 years of brass band contests in New Zealand, 1880-1980. Powerbrass Music for the Brass Band Association of New Zealand. https://natlib-primo.hosted.exlibrisgroup.com/permalink/f/1s57t7d/NLNZ_ALMA21242590750002836
Quickstep. (1920a, 23 October). Bandsmen’s Gossip : Celebrated Conductor. Herald (Melbourne, Vic. : 1861 – 1954), 4. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article242245731
Quickstep. (1920b, 24 July). Bandsmen’s Gossip : Leader of Two Famous Bands. Herald (Melbourne, Vic. : 1861 – 1954), 11. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article242308343
Royal South Street Society. (1915). 1915-10-23 Brass Band Contests : Held at City Oval [Eisteddfod Results]. Royal South Street Society Results Database. https://results.royalsouthstreet.com.au/results/1915-10-23-brass-band-contests
Royal South Street Society. (1920). 1920-10-23 Brass Band Contests [Eisteddfod Results]. Royal South Street Society Results Database. https://results.royalsouthstreet.com.au/results/1920-10-23-brass-band-contests
Royal South Street Society. (1921). 1921-10-22 Brass Band Contests : Held at City Oval [Eisteddfod Results]. Royal South Street Society Results Database. https://results.royalsouthstreet.com.au/results/1921-10-22-brass-band-contests
Royal South Street Society. (1922). 1922-10-26 Brass Band Contests [Eisteddfod Results]. Royal South Street Society Results Database. https://results.royalsouthstreet.com.au/results/1922-10-26-brass-band-contests
TOUR-SCHEME LAUNCHED : £2000 Already Raised for Band. (1923, 15 June). Herald (Melbourne, Vic. : 1861 – 1954), 9. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article244032124
TWELVE YEARS OF HARMONY. (1923, 15 June). Sun News-Pictorial (Melbourne, Vic. : 1922 – 1954; 1956), 13. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article274146118
VICTORIAN BAND : TO PLAY AT WEMBLEY. (1924, 07 January). Daily Mail (Brisbane, Qld. : 1903; 1916 – 1926), 10. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article217628364
Warren, W. H. (1924). The Famous St. Hilda Colliery Band : World Champions : 1912 – 1920 – 1921 – 1924 [Postcard]. [Formal]. W. H. Warren, South Shields, U.K.
WORLD TOUR DROPPED : Malvern Band Disappointed : LACK OF FUNDS. (1923, 28 September). Geelong Advertiser (Vic. : 1859 – 1929), 3. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article166022301
Young, G. (1922, 04 December). MUSICAL DYNAMOS : Malvern Band at Practice : Preparing for World Tour. Herald (Melbourne, Vic. : 1861 – 1954), 9. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article246671641
Young, G. (1923a, 06 June). BAND OF BANDMASTERS : TO THE EDITOR. Herald (Melbourne, Vic. : 1861 – 1954), 10. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article244030215
Young, G. (1923b). The Malvern Tramways Band : An Appreciation. In Community singing : St. Kilda Esplanade every Wednesday evening : words of songs & program (pp. 24). Malvern Tramways Band. http://nla.gov.au/nla.obj-52777212
Young, G. (1923c, 23 April). MALVERN TRAMWAYS BAND TOUR : To The Editor of the Argus. Argus (Melbourne, Vic. : 1848 – 1957), 3. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article1892296
Young, G. (1923d, 27 April). MALVERN TRAMWAYS BAND WORLD TOUR : (To the Editor). Prahran Telegraph (Vic. : 1889 – 1930), 7. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article165130459
Young, G. (1923e, 25 April). MALVERN TRAMWAYS BAND WORLD TOUR : TO THE EDITOR OF THE AGE. Age (Melbourne, Vic. : 1854 – 1954), 12. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article204072904
Young, G. (1923f, 10 February). MUSICAL RIVALRY : Malvern Band Superior to Sydney Players. Herald (Melbourne, Vic. : 1861 – 1954), 7. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article243800219
Young, G. (1923g, 22 May). PEOPLE SAY—- : “Tristan’s” Triteness. Herald (Melbourne, Vic. : 1861 – 1954), 8. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article244031836
Young, G. (1923h, 17 January). PEOPLE SAY…. : COMMUNITY SINGING : To THE EDITOR. Herald (Melbourne, Vic. : 1861 – 1954), 6. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article246668892
Young, G. (1924, 19 November). AT CRYSTAL PALACE : Great Band Contest : AUSTRALIA THIRD. News (Adelaide, SA : 1923 – 1954), 6. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article129811157
Zealley, A. E., & Ord Hume, J. (1926). Famous Bands of the British Empire : Brief Historical Records of the recognized leading Military Bands and Brass Bands in the Empire. J. P. Hull. https://catalogue.nla.gov.au/catalog/4808576