Introduction:
In comparison to the first part of this series of posts, the Australian bands were not quite as proactive as crossing the Tasman as their New Zealand counterparts. When the Australian bands did go to New Zealand, they tended to do very well in competition and performances gained rave reviews. This part of the post will detail the trips that four Australian bands made to New Zealand between 1900-1940.
1907: Newcastle City Band – Christchurch International Exhibition Contest:

It took a little bit longer for Australian bands to start reciprocal visits to New Zealand and in 1907 the then champion Newcastle City Band traveled to Christchurch via Wellington to participate in the International Exhibition Contest (“NEWCASTLE CITY BAND.,” 1907). By all accounts, this was a huge event with no less than twenty-nine bands participating (Newcomb, 1980). Also in attendance at the Exhibition was the world-famous Besses O’ Th’ Barn Band from England who performed to great acclaim (Newcomb, 1980). Code’s Melbourne band was also intending to take part in the event however they did not end up going due to some of their bandsmen being unable to take time off work (Trombone, 1907).
The Newcastle Band achieved a very credible third placing against some top-ranking New Zealand bands and some of their soloists also achieved good placings (“BAND CONTEST,” 1907). However, soon after the contest finished, questions were being asked over the judging with Newcastle and others feeling that Newcastle should have been placed higher. In an article published in the Wanganui Herald newspaper, a Mr. Edgar Nicholas from Ballarat who was visiting was asked about the adjudicating at the contest by Lieutenant Bentley, formerly of England. Mr. Nicholas said in his interview that,
I have been at all the band contests in Ballarat, where the principal bands in Australia compete. We had had Messrs Ord-Hume, Wade, and Beard from England, but, speaking generally, Mr. Bentley has given equal satisfaction in Ballarat with these gentlemen”.
(“THE JUDGING AT THE CONTEST,” 1907)
Speaking pragmatically in the interview, Mr. Nicholas noted that an adjudicator sometimes fails to please everyone given that Mr. Bentley had to judge 30 bands. Also, as Mr. Nicholas suggests, some bands may not have been at their best given the late hours that some of them competed (“THE JUDGING AT THE CONTEST,” 1907). Mr. Nicholas kept drawing comparisons with the Ballarat South St. Eisteddfod, the first being that that in the case of large sections, Ballarat employed up to three judges and that in Australia there were separate gradings which, at the time, were not used in New Zealand (“THE JUDGING AT THE CONTEST,” 1907).
One Newcastle bandsman was quite firm in his comments which were published in a Newcastle Morning Herald and Miners’ Advocate newspaper article,
When our band-master tells us we played well I am satisfied. He tells us often enough when we don’t play well; but we never played better than in the competition.”
(“THE CITY BAND.,” 1907).
Aside from this issue over the placings, most accounts note that the Newcastle City Band had an enjoyable trip and were welcomed in various locations. On the ship home, they played for an appreciative audience and were welcomed home with a civic reception (“THE CITY BAND.,” 1907).
| Band: | Own Choice: | Test: | Total: |
| Wanganui Garrison | 158 | 147 | 305 |
| Kaikorai Brass | 158 | 145 | 303 |
| Newcastle City | 156 | 146 | 302 |
1923: Redfern Municipal Band – South Island Brass Band Association Contest, Dunedin:
Some sixteen years after the first Australian band traveled to New Zealand, it took until 1923 for the next Australian band to arrive. The Redfern Municipal Band, conducted by Mr. W. Partington, was a formidable band at the time and they undertook a short tour through the South Island of New Zealand on their way from Wellington to Dunedin. Upon arriving in Wellington, along with a contingent of N.S.W. Bowlers, they were given a large civic reception by the Mayor (“BOWLERS AND BANDSMEN,” 1923). The arrival of Redfern had generated an amount of excitement throughout New Zealand, suffice to say that their conductor Mr. W. Partington had conducted one of their own champion bands, The Wanganui Garrison Band for a while (“ENTERPRISING BAND,” 1923; Newcomb, 1980) – the band from Redfern was not unknown in New Zealand.
Redfern Municipal was ultimately triumphant in Dunedin by winning the A Grade section and Aggregate. This was no easy feat given that a number of New Zealand’s A grade bands were in the section, including Mr. Partington’s former band, Wanganui. Newcomb (1980) wrote of Redfern and the A Grade contest,
In Dunedin, it competed against seven of New Zealand’s top A grade bands. After a week of intensive rehearsal in the “Edinburgh of the South” Redfern was rewarded for its painstaking efforts when it took out the A grade title 12 points ahead of Invercargill’s Hiberian Band. The 1st Canterbury Mounted Regiment Band was third.
The talking point of the contest was the poor performance of the Wanganui Garrison Band, under Mr. J. Crichton. The veteran Wanganui conductor’s ambition was to thrash the Redferners…”
(p. 44)
Of course the triumph was noted in Australian and New Zealand newspapers, and rightly so, it was a great win for the Redfern band (“BAND CONTEST,” 1923; “REDFERN BAND,” 1923). However, the backstory of the two conductors was intriguing and written up as part of an article published by the NZ Truth newspaper:
There is an interesting story (perhaps) behind the crossing of the Redferners. Bandmaster Partington was over here for a while, and had charge of the Wanganui Band. Within a very short period of training under his baton he made champions of them, winning the N.Z. honors last year. Then there arose a controversy between Partington, of Aussieland and Jim Crichton, of Wanganui, the ex-bootshopman who knocked off trade to become a musician, undergoing a special course of study in London for the purpose of pursuing his brass-bound hobby. He told P. that if he (C.) had the Woolston Band under his baton for a month he could beat anything that P. could bring against it. There was such a heated argument that it was leading to something like a £1000 wager. But P. left for Aussieland again, and took charge of the Redferners. Now the question is: Did he bring the Sydneysiders over to compete against anything that Jim Crichton had under his wing? Well, Jim took the Wanganui cracks down to Dunedin to play against their old leader – and Wanganui was nowhere in the final!
(“Brass Bands and Bandsmen,” 1923)
When returning to Australia, there was a snippet of thought that the Redfern Band might head to England to compete (“REDFERN BAND,” 1923). However, this evidently did not eventuate. Their conductor, Mr. Partington, went on to other activities and formed a representative band that travelled Australia with the aim of heading to England. But as detailed in a previous post, that tour ended up running out of money upon arrival in Perth.
1925: Malvern Tramways Band – New Zealand National Band Championship, Auckland:
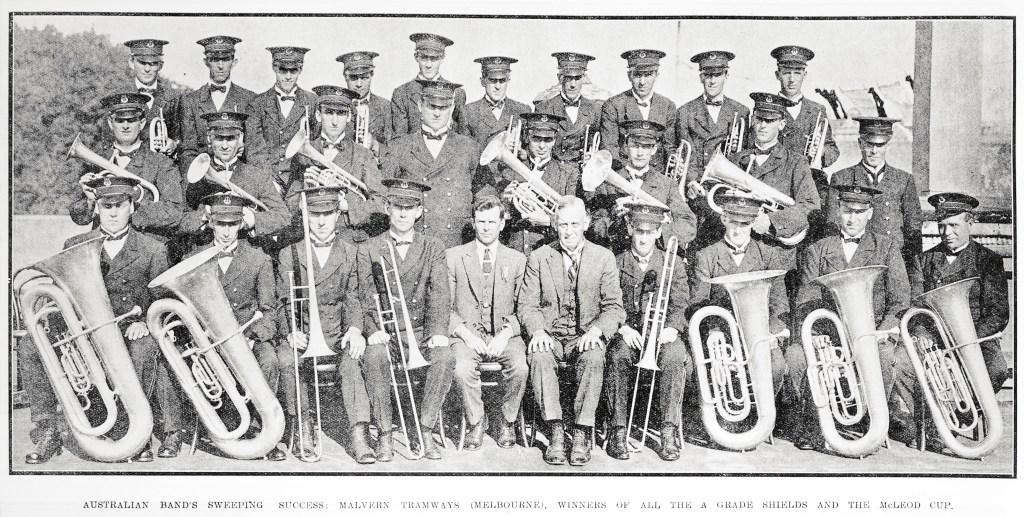

Just two years later, another crack Australian band made the trip to New Zealand to compete. The Malvern Tramways Band was renowned throughout Australia as one of the elite bands of the Commonwealth having won numerous competitions by this time. So much so that the Malvern Band, like many others, tried to get to England however they too were unable to raise sufficient funds. To compensate, they did arrive in New Zealand early in 1925 to commence a six-week tour culminating in the championships in Auckland (“Malvern Tramways Band,” 1925d).
The reputation of Malvern preceded them to New Zealand and all manner of hospitality was afforded for the band including, special observation cars on trains, reduced rail fares and free travel on New Zealand trams! (“MALVERN TRAMWAYS BAND,” 1925b). They sailed from Melbourne to Invercargill and from there travelled up to Auckland giving concerts in all the major towns on the way (“MALVERN TRAMWAYS BAND,” 1925a). By late February they had reached Auckland and commenced competing in the band sections and solo sections. In competition, the Malvern Tramways band was formidable and they won just about every section except for the Quickstep where they achieved third place (“MALVERN TRAMWAYS BAND.,” 1925b; “MALVERN WINS A GRADE TEST,” 1925). Newcomb (1980) wrote of the contest:
After many years of bickering, common sense prevailed when the North and South Island associations joined forces to stage the 1925 national contest in Auckland.
It was made doubly interesting by the presence of the Malvern Tramways Band from Australia under the conductorship of Mr. Harry Shugg.
New Zealand’s top A grade bands proved no match for the highly fancied Australian combination which won both tests, the hymn and the championship aggregate.
(p. 45)
After this astounding success in New Zealand, the Malvern Tramways Band sailed for Sydney where they performed their competition repertoire in concert to rave reviews (“MALVERN TRAMWAYS BAND,” 1925c). Traveling back to Melbourne, the success of their New Zealand venture was written up a couple of months later by the local Prahran Telegraph newspaper (“MALVERN TRAMWAYS BAND.,” 1925a).
1936: Cairns Citizens’ Band – New Zealand National Band Championships, New Plymouth:
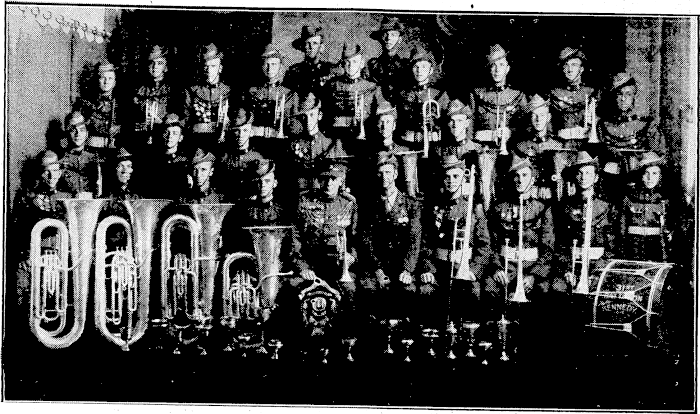
In October 1935, the Cairns Post newspaper published the news that the Cairns Citizens’ (31st Battalion) Band would compete at the 1936 New Zealand Band Championships in New Plymouth (“MAKING HISTORY.,” 1935). Conducted by James Crompton, a person that was not unfamiliar to the New Zealand brass bands, the band was nominally the first band from Queensland to compete in New Zealand and the first from Australian Military Forces (“MAKING HISTORY.,” 1935).
The Cairns Citizens’ Band won the New Zealand Championship that year, although they did not win the Test selection. However, their aggregate points were enough that they could win the championship (“Cairns Band.,” 1936; Newcomb, 1980). The New Zealand press was also impressed by the standards set in New Plymouth and an article published in the Evening Post newspaper praised the marching – the Cairns Citizens’ Band achieved 2nd place in the marching section (“GOOD MARCHING,” 1936).
Conclusion:
There was a similarity of experiences for bands crossing to either side of the Tasman; with civic receptions, a very interested and informed public and commentary from the newspapers. The excitement generated by viewing a visiting band was also interesting to note – and there were plenty of other articles that were written about bands (but too many to list in these posts)! It was interesting to note just how close the Australian and New Zealand brass band movements were in terms of standards and rules, so much so that any band crossing the Tasman could expect near similar conditions of competition. The best bands of each country could match the other and in the spirit of competition, this was plain to see.
It is the collegial nature of band movements that enabled these visits to happen and to this day, the friendly rivalries remain, and visits continue to take place. Kudos to the bands that made these early trips as they set a foundation for other bands to build on.
<- Part One – New Zealand Bands in Australia
References:
Auckland Weekly News. (1925). AUSTRALIAN BAND’S SWEEPING SUCCESS : MALVERN TRAMWYS (MELBOURNE), WINNERS OF ALL THE A GRADE SHIELDS AND THE McLED CUP. In Auckland Weekly News (AWNS-19250305-46-01 ed., pp. 46). Auckland, N.Z. https://kura.aucklandlibraries.govt.nz/digital/collection/photos/id/244635/rec/1 Ngā Pātaka Kōrero o Tâmaki Makaurau / Auckland Libraries Heritage Collections.
AUSTRALIAN BAND FOR NEW ZEALAND CONTEST. (1935, 23 November). Evening Post. https://paperspast.natlib.govt.nz/newspapers/EP19351123.2.26.1
BAND CONTEST : Redfern Win The Aggregate : Wellington Watersiders Third. (1923, 24 February). Evening Post. https://paperspast.natlib.govt.nz/newspapers/EP19230224.2.68
BAND CONTEST : Winners of Competitions. (1907, 16 February). New Zealand Times. https://paperspast.natlib.govt.nz/newspapers/NZTIM19070216.2.61
BOWLERS AND BANDSMEN. (1923, 08 February). Evening Post. https://paperspast.natlib.govt.nz/newspapers/EP19230208.2.25
Brass Bands and Bandsmen. (1923, 03 March). NZ Truth. https://paperspast.natlib.govt.nz/newspapers/NZTR19230303.2.2.4
Cairns Band : Wins Championship. (1936, 02 March). Daily Mercury (Mackay, Qld. : 1906 – 1954), 6. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article172909750
THE CITY BAND. (1907, 27 February). Newcastle Morning Herald and Miners’ Advocate (NSW : 1876 – 1954), 5. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article136605589
ENTERPRISING BAND : Sydney Competition Band Likely to Visit Wanganui. (1923, 12 January). Hawera & Normanby Star. https://paperspast.natlib.govt.nz/newspapers/HNS19230112.2.17
GOOD MARCHING : Port Nicholson Band : Recent National Contest. (1936, 09 March). Evening Post. https://paperspast.natlib.govt.nz/newspapers/EP19360309.2.25
THE JUDGING AT THE CONTEST. (1907, 15 February). Wanganui Herald. https://paperspast.natlib.govt.nz/newspapers/WH19070215.2.32
MAKING HISTORY : Band For New Zealand : Cairns to Cross Tasman. (1935, 02 October). Cairns Post (Qld. : 1909 – 1954), 5. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article41708070
MALVERN TRAMWAYS BAND. (1925a, 20 February). New Zealand Herald. https://paperspast.natlib.govt.nz/newspapers/NZH19250220.2.132
MALVERN TRAMWAYS BAND. (1925b, 20 January). Herald (Melbourne, Vic. : 1861 – 1954), 16. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article243874312
MALVERN TRAMWAYS BAND. (1925c, 10 March). Sydney Morning Herald (NSW : 1842 – 1954), 10. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article16207234
Malvern Tramways Band : Leaves for New Zealand. (1925d, 13 February). Prahran Telegraph (Vic. : 1889 – 1930), 8. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article165132427
MALVERN TRAMWAYS BAND : Recent New Zealand Tour : Success in Competitions. (1925a, 22 May). Prahran Telegraph (Vic. : 1889 – 1930), 6. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article165141099
MALVERN TRAMWAYS BAND : Wins Championship of New Zealand. (1925b, 06 March). Prahran Telegraph (Vic. : 1889 – 1930), 7. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article165137387
MALVERN WIN A GRADE TEST. (1925, 27 February). Evening Post. https://paperspast.natlib.govt.nz/newspapers/EP19250227.2.83.1
New Zealand International Exhibition. (1907, 12 February). Star, 3. https://paperspast.natlib.govt.nz/newspapers/TS19070212.2.57.2
The Newcastle (N.S.W.) City Brass Band; Champion Band of Australia, At Present Visiting New Zealand. (1907, 13 February). New Zealand Mail. https://paperspast.natlib.govt.nz/newspapers/NZMAIL19070213.2.235.6
NEWCASTLE CITY BAND : Going to New Zealand. (1907, 29 January). Newcastle Morning Herald and Miners’ Advocate (NSW : 1876 – 1954), 5. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article136608558
Newcomb, S. P. (1980). Challenging brass : 100 years of brass band contests in New Zealand, 1880-1980. Powerbrass Music for the Brass Band Association of New Zealand.
REDFERN BAND : New Zealand Triumph. (1923, 09 March). Evening News (Sydney, NSW : 1869 – 1931) ,8. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article118834570
Trombone. (1907, 09 February). The Exhibition : The Band Contests. Lyttelton Times. https://paperspast.natlib.govt.nz/newspapers/LT19070209.2.71




































