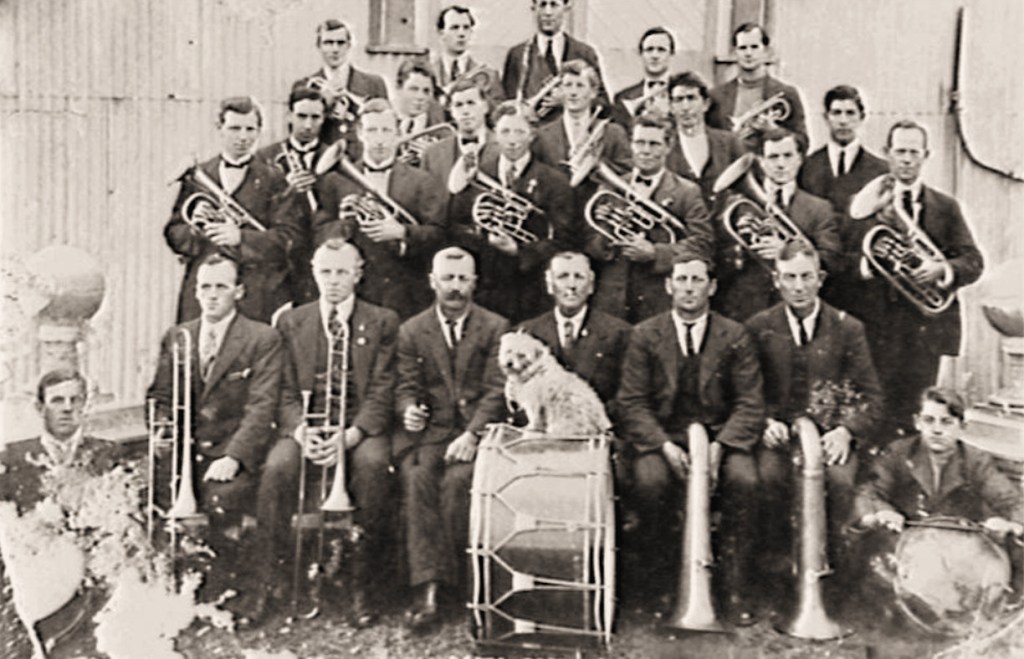
Introduction:
The visit of one of the premier bands of Britain to Australia would be an event of great interest, and Mr. Hume, speaking on the matter, said that if the railways would guarantee to grant free passes to the members, he could almost promise that either the Besses o’ th’ Barn Band, of Lancashire or the Black Dyke Band, of Yorkshire, would come out. That the venture would be a success Mr Hume says he has not the slightest doubt, and he considers that the playing would come as a revelation to Australians.
(“MR. J. ORD HUME.,” 1903)
Australian bands, to put it simply, are an extension of the movement started in Britain and bands are one of Britain’s great cultural exports. As has been noted in other posts, the influx of people from the British Isles and other places carried their music with them. It is no surprise that in the early years, bands were established in localities across Australia.
There was no shortage of enthusiasm for starting a band, and no shortage of budding musicians willing to learn. However, training them, supporting them and giving them inspiration was at times problematic. Musical training was sometimes left up to those willing to take the job of bandmaster, whether they had brass band skills or not. This was the case in some places but not others as some bands became very proficient, very quickly.
Not that this mattered to some untrained ears. Many towns and localities were simply glad to have a band (a source of civic pride). Although the bands that were founded in the late 1800s and early 1900s possibly realised that their playing was not up to English standards. Bands were willing to learn, it was just a matter of whom to learn from. It was not until the advent of organised competitions and visits from English bands that the standard of playing was given a critical ear and adjudicators provided bands with helpful comments on how to improve.
This post will examine what was probably the greatest shift in musical standards amongst Australian bands that took place over the period of two to three decades. This rapid improvement was partly inspired by the visits of the eminent Scottish band adjudicator James Ord Hume and the famous Besses o’ th’ Barn Band from England. Thankfully, for the purposes of this post, we can see the comments of James Ord Hume over the course of his two visits as he judges the bands. We will also see that while the tours of Besses were significant in themselves, it is the lasting effect these visits had on Australian bands that deserves attention. This is a combined story; a story of how British band musicians did their best to inspire and help Australian bands to be the best they could be.
James Ord Hume, 1902-1903:

Lieutenant James Ord Hume was an “eminent English and Scottish bandmaster, composer, critic and adjudicator” (Mullen, 1965, p. 40). A lifetime of musical training in the British Army and civilian bands had provided him with a unique connectedness with all sorts of musicians, and he had utilised his opportunities to the full by learning to play all band instruments and study musical theory (Thirst, 2006). His reputation as a musician preceded him and he was highly sought after as an adjudicator and clinician. As Thirst (2006) writes in his book ‘James Ord Hume 1864-1932 : a friend to all bandsmen : an account of his life and music’,
He was a popular adjudicator throughout the British Empire, and frequently visited Australia and New Zealand to judge in the famous contest at Ballarat and elsewhere
(p. 47)
This was not an idle statement as many accounts of James Ord Hume show him to be a very forthright person with his adjudications and opinions, and he was appreciated by bandsmen all over Australia and New Zealand (“Bathurst Band Contests.,” 1902). One might say that with his attitude he was a bit free with his advice. Nevertheless, Ord Hume acted with the best intentions and sought to bring the standards of Australian bands up to where he thought they should be and provided solutions on how Australian bands might achieve this. Certainly, his foretelling that Australian bands would view the “playing” of Besses o’ th’ Barn Band as a “revelation” came to fruition some years later (“MR. J. ORD HUME.,” 1903).
When Ord Hume talked, Australian bandsmen listened and there are some notable examples of his advice being applied literally and quickly. He greatly followed developments in the brass band world, and it is because of him that Australian bands stopped using valve trombones – Ord Hume could not stand them. The article below published by the Molong Argus newspaper is testament to his comments, and it seems James Ord Hume was quite happy to repeat this mantra to whomever asked him about it (“About Trombones.,” 1902; “Bathurst Band Contests.,” 1902).

James Ord Hume first visited Australia in 1902-1903 where he adjudicated at various eisteddfods around the country, starting with the South Street band sections in Ballarat. Ord Hume was greatly impressed with the concept of the South Street and before the competitions had even begun, he had given them praise – and also a taste of what to expect.
He said he had always had a desire to visit Australia, and only demurred on receiving the invitation from the South-street Society to adjudicate at this year’s contests because of want of time. However, the musical people of England wanted to know how they stood with Australia in competitive work, and the mission he entered upon was to give a candid opinion of all that occurred in a general report. The musical contests of South-street were certainly the greatest in the world.
(“SOUTH-STREET COMPETITION’S,” 1902)
It would be fair to say that, barring some exceptions, he was not overly impressed with what he heard in the band contests and was quite clear about this in his comments (“BALLARAT COMPETITIONS.,” 1902). His parting comments were a measure of contrast. Of the good bands he said…
…had given splendid performances which would compare favourably with the best heard at contests in the old country.
(“BALLARAT COMPETITIONS.,” 1902)
And he was scathing about bands at the other end of the scale…
On the other hand some were distinctly bad. Their principal fault was a lack of tone; the men had not blown out their instruments as they should have done. If a player just obtained a good loud tone he could easily subdue it without losing breath and character. In the constant effort to play softly this was all lost.
(“BALLARAT COMPETITIONS.,” 1902)
This being said, he also offered practical advice on how bandsmen could improve.
To obtain tone he advised bandsmen to practise slow scales, and plenty of steady moving psalm tunes.
(“BALLARAT COMPETITIONS.,” 1902)
Timothy Thirst (2006) did note in his book that Ord Hume was “known to be sometimes rather sarcastic and outspoken in his comments.” (p. 55).
Ord Hume provide similarly forward comments when adjudicating in Bathurst, Sydney and New Zealand for various competitions, such was the hectic schedule of his visit. However, there are some indications that Australian bands were beginning to pick up their musical standards. After adjudicating in Sydney at the end of 1902, Ord Hume provided some observations.
He said that since he had been in Australia he had noticed an improvement in the playing of the bands. He had observed at Ballarat and Bathurst, and now here. He was about to proceed to Castlemaine (Vic.), and thence to New Zealand, and on his return the results of his observations would be published.
(“CHAMPIONSHIP BAND CONTEST.,” 1902)
When Ord Hume returned to Ballarat in 1903 prior to his travel back to England, he was asked what Australian bands needed to do to achieve a more excellent standard of playing.
“They require tuition” he said. “In many cases it has come to this, that the men have to come to know as much as the conductor himself, and in such a case the progress made is not very great as you may imagine. In New Zealand this fact is not so noticeable and it explains the reason why their bands, generally speaking, are much better than those here. They possess over there many instructors who have come out from the old country, but here it seems to be ‘Australia for the Australians,’ and that will not do in music at any rate.”
(“MR. J. ORD HUME.,” 1903)
As mentioned, Ord Hume was appreciated for his direct commentary and aside from his work adjudicating he was afforded all kinds of civic receptions at the conclusion of events. Perhaps this is understandable given his status as an eminent musical authority, but it was also for his honesty – what he said, he said with conviction. Granted, some bandsmen might have been offended. But in his own way he was trying to educate. Band Associations were very pleased to have someone of that calibre adjudicate which is why, after the 1902 Ballarat event he was made an Honorary Life Member of the Victorian Bands’ Association (“SOUTH STREET SOCIETY.,” 1902).
Frank Wright, the great Australian-born bandsman, summed up the first visit of Ord Hume to Australia when he wrote an appreciative article in the June 15th, 1935 edition of British Bandsman after Ord Hume’s passing.
No other event in band history, except, perhaps the tour of the famous Besses o’ th’ Barn Band, can be compared with his visit, as having equal influence in setting the standard for Australian bands. He encouraged the young ambitious bandsman, and it was this personal interest that endeared him to the Australian people.
(Wright, 1935, p. 4)
If Ord Hume was an instigator of change in the way Australian band did things, the tours of Besses fanned further improvement as they provided a practical example of how an elite band sounded and operated. The Besses band was no stranger to Ord Hume and it appears there was some mutual admiration and respect. Ord Hume even arranged a Polka for Besses which can be heard below (Besses o’ th’ Barn Band Channel, 2022). This radio broadcast recording from 1940, played by the City of Ballarat Municipal Band was provided to the Besses band by the Ballarat Band historian Bob Pattie, and uploaded to YouTube by the historian of the Besses o’ th’ Barn Band, Stephen Hughes – thank you both! (This video was updated in January 2022)
Besses o’ th’ Barn Band, 1907 & 1910:

The tours:
Much of the particulars of the two Besses tours were detailed in a previous post (de Korte, 2018a). In summary, the famous Besses o’ th’ Barn Band from Lancashire undertook two massive tours in the space of three years which took them all over the globe (Besses o’ th’ Barn Band, 2018). While in Australia, they were afforded concerts and engagements in towns and cities all over the country and never failed to please audiences – such was their reputation (“BESSES O’ TH’ BARN BAND.,” 1907a; “BESSES O’ TH’ BARN BAND.,” 1907c). Civic welcomes were par the course and the photo above of the parade turning the corner from Collins Street to Swanston Street at the Melbourne Town Hall is a case in point. Besses were greeted at Spencer Street Station by a combined twenty-two bands directed by Edward Code which led them in a procession up Collins Street to the Town Hall (“BESSES O’ TH’ BARN BAND.,” 1907e). It is said that 70,000 people turned out to watch this procession, which would have been an amazing sight to see! (“Besses o’ th’ Barn Band,” 1907).

Besses toured Australia again in 1910 and during this tour, lead Cornetist William Ryder left the band to join a local theatre ensemble and then became the first bandmaster of the then Prahran & Malvern Tramways Employees Band in 1911 (de Korte, 2018b; Quickstep, 1920b). Cornetist Percy Code, son of Mr Edward Code, took his place on the tour (Quickstep, 1920a). The Herald weekly columnist ‘Quickstep’ provides some insight into this development through separate articles which detail the band lives of William Ryder…
Leaving England as principal cornet soloist with the famous Royal “Besses o’ th’ Barn” Band on their second world tour, Mr Ryder left the band on the completion of its Victorian trip and settled in Melbourne. He was immediately engaged to play solo cornet in a picture theatre orchestra.
(Quickstep, 1920b)
…and Percy Code.
At the time the famous “Besses o’ th’ Barn” Band was touring Australia and Percy Code was offered an engagement which he accepted. While he was abroad, his brilliant playing was favourably commented on by British press. One leading band journal styled him “Percy Code the golden-toned,” also crediting him as one of the finest cornetists in England. Study in orchestration and composition was undertaken, under the guidance of Mr Alexander Owen, of Manchester, known as the greatest authority on brass band music in the world.
(Quickstep, 1920a)

Mr Alexander Owen at the time was the conductor of Besses during the first tour and part of the second tour and he was highly regarded in Australia and around the world – newspapers of the day were effusive in their praise, the Evening Telegraph newspaper from Charters Towers being one of them (“Mr. Alexander Owen.,” 1907). After the tour, the Assistant Conductor of Besses, Mr Christopher Smith accepted a position as conductor of the Adelaide Tramways Band (Seymour, 1994).

By all accounts, the two tours of the Besses band were huge successes and they opened up the ears and eyes of all who heard them.
The influence:
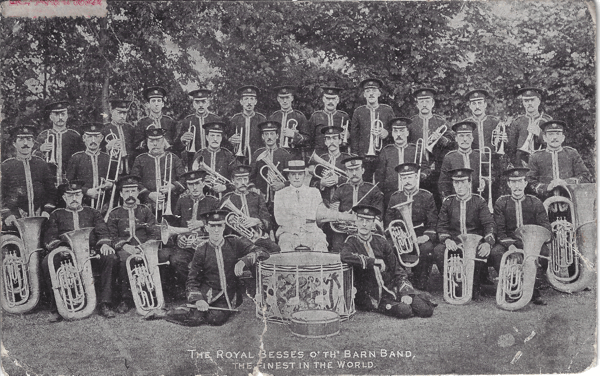
Besses o’ th’ Barn Band made a lasting impression on the Australian band movement. Notwithstanding their reputation prior to their visits to Australia, they certainly grew in stature on this unique part of their tours. One hallmark of their visits was the fact they were very much a band full of critical listeners, teachers, advocates and gentlemen who were always willing to offer advice and help.
Hundreds of newspaper articles were published during the two Besses tours, so it is impossible to reference them all. Buried in these articles are hints of information as to how the visits were perceived by Australian bandsmen, and what they learnt from the visiting band. In July 1907 the Besses band were giving a concert in Goulburn, New South Wales and after the concert they were entertained by the local Australian Horse Band. The Mayor of Goulburn was also present at this supper and his comments were noted in an article published by the Goulburn Herald.
He welcomed then not merely as bandsmen from the old country, but as brothers, and hoped their stay here would be a pleasurable one. He was sure it would be great value from an educational point of view to the bands in Australia. […] He hoped with all sincerity that the visit of the Besses would be crowned with the success it deserved, and that they would be able to say that the Australians were a loyal and patriotic people – which they were right up to the hilt – and pleased to accord their support to organisations such as the Besses o’ th’ Barn Band, which came so far to educate them.
(“BESSES O’ TH’ BARN BAND.,” 1907a)
It is interesting to note the language here from the Mayor of Goulburn, not so much for the comments on patriotism but the words on education. Besses were not really touring to educate Australia bands per se however, that was an inadvertent effect of them being in Australia. Further comments were made by Mr. Cody, Bandmaster of the Australian Horse Band in the same article.
The visit of Besses could have none other than a good effect on band music in Australia. The various bands would be moved to do greater things than in the past, and they result would be beneficial all round.
(“BESSES O’ TH’ BARN BAND.,” 1907a)
Besses visited Adelaide in August 1907 and comments made in the Register newspaper were equally full of expectation on what the Besses visit would mean for Australian bands.
…the Besses’ performances must unquestionably stimulate band music in the State, which has been the case of every town they have visited on the Australian tour. The artistic methods employed by Mr. Owen in conducting the Besses in their playing are said to be a revelation in technique and phrasing, and have been described by a leading Sydney bandmaster as being “an entirely new musical language for colonial bands to study”.
(“BESSES O’ TH’ BARN BAND.,” 1907c)
After touring Australia for a couple of months, in September 1907, Besses were in Bendigo and in an article published by the Bendigo Advertiser, perhaps, we can see some real analysis and insight into the benefits the Besses visit would bring to Australian bands.
There are two things which especially distinguish the Besses. In the first place the high degree of finish that characterises their playing, so that all bandsmen that have heard them have confessed that something new in band music had been revealed to them, possibilities in brass that were previously undreamed of, and in the second place, the courteous and obliging urbanity in which the conductor, Mr. Alexander Owen, and members of his corps, have done whatever they could to help those colonial bands which have appealed to them for advice and instruction. The present generation of bandsmen will never forget their impression of the Besses, which will more or less in the future influence their aspirations and efforts, and when a young generation of Tubal Cains grow up, whose lips are not yet too tender for the resounding brass, they will hear abundant reminiscences of how this or that passage was taken up by the Besses, until not impossibly, they will wish that at last that the Besses had never toured through Australasia.
(“BESSES O’ TH’ BARN BAND.,” 1907b)
As mentioned, Besses undertook a second world tour and in 1910 they were back in Australia. Alexander Owen stepped down from his conducting duties during this tour and Mr Christopher Smith took over to no less acclaim from audiences, such was the ability of this ensemble. Australian bands were also changing, and this had been noticed by various writers, which was attributed by the visit of Besses three years before. Said a writer in an article published by The Ballarat Star newspaper in June 1910.
It might truthfully be said that the standard of band music underwent an appreciable change for the better as the result of the visit of this celebrated combination.
(“AMUSEMENTS.,” 1910)
Mr. W. Bogle, manager of the Besses band during their second tour provided some interesting comments comparing band movements of the U.K. and Australia in a wide-ranging interview which was published by the Evening News newspaper in August (“THE MUSIC OF THE BAND.,” 1910). While his interview is too much for this post, the advice he provided was obviously valuable to the Australian band movement. And again, there were indications that Australian bands were heading the right way.
They had no doubt that the public of Australia would encourage the improvement of brass bands, and it was particularly pleasing to see they were assisted by the municipal bodies.
(“THE MUSIC OF THE BAND.,” 1910)
The legacy:
The influence of the Besses tours should not be viewed as just bands and band members attending their concerts or being instructed, advised and then feeling very much inspired. It can also be seen in other ways. William Ryder, Percy Code and Christopher Smith, bandsmen who had all been associated with Besses at high levels brought the Besses influences with them to their own bands, playing and adjudication. Australian bands began to rapidly improve after the first Besses tour and inspiration from the band itself. Instruction and adjudication from these men helped carry things further. Mr Christopher Smith, once a deputy conductor of Besses, gave high praise to certain bands and was in no doubt that Australian bands could compete with the best (“WOULD CAPTURE LONDON,” 1922). He adjudicated at South Street in 1922 and gave a general comment on the standards that were set.
“The standard was appreciably higher than when I judged bands here two years ago.” He said, “and what is pleasing to me is to find the unsuccessful bands more closely approaching the standard set by the victorious bands in all the grades.”
(“WOULD CAPTURE LONDON,” 1922)
He left his highest praise for the famous Malvern Tramways Band which had just won all the A Grade band sections of the 1922 South Street competition.
Malvern Tramways Band is such a cultured musical combination that it would capture English audiences by its playing. It would do so by sheer merit.
(“WOULD CAPTURE LONDON,” 1922)
And in a final remark he highlighted advancements of bands in the lower grades.
Mr Smith went on to say that marked advances had been made by the “B” grade and “C” grade bands in their contest pieces.
(“WOULD CAPTURE LONDON,” 1922)
High praise indeed and this provided a good indication of where Australian bands were at, and where they were going just over a decade from the last Besses tour. The bands were definitely improving!
Interestingly, the tours of Besses were still being talked about in the early 1930s as the legacy of the visits still resounded in the band movement. The Daily News newspaper in Perth published an article in September 1930, essentially on Mr Hugh McMahon, the genius Cornetist but also mentions the state of brass bands in Western Australia as a whole. The article also had this to say about the legacy of the Besses tours.
Most memorable had been the visit of the Besses of the Barn Band which had shown what a brass band could do in the way of interpreting certain classes of music. The visitors had given a revelation of the playing of hymn tunes equal to that of any organ and had set a new view before Australian players.
(“EMPEROR OF CORNET,” 1930)
To finish this section on the Besses tours and the influence they left behind, we have these comments from a person speaking at the annual banquet of the Queensland based Howard and Torbanlea Citizens’ Band in December 1933.
After a loyal toast, the toast of the Howard and Torbanlea Citizens’ Band was proposed by Mr. G. J. Edmunds who stressed the many advantages of having a band in the community. Mr. Edmunds declared that the visit of the Besses o’ th’ Barn Band many years ago was the running point in the standard of band throughout the Commonwealth, and today, quite a number of bands had reached that standard.
(“BAND BANQUET,” 1933)
Australian bands had begun to reach the pinnacles set by Besses. And in the 1920s, with tours to England by the Newcastle Steelworks’ Band and the Australian Commonwealth Band, both conducted by Albert Baile, Australian bands proved they could match the much-vaunted English bands and win their competitions (Zealley & Ord Hume, 1926).
A side note, Mr John Dixon, Agent for Boosey & Co.:
James Ord Hume provided much advice to the Australian band movement on how to improve, and the Besses o’ th’ Barn Band clearly displayed an excellence in musicianship. One aspect that could be considered is that Australian bands needed the best of instruments and British instrument manufacturers saw opportunities in Australia & New Zealand for additional sales. Travelling with James Ord Hume in 1902 and on the first Besses tour in 1907 was an agent for the Boosey & Co. instrument manufactures, Mr John Dixon (“MUSIC ADJUDICATOR,” 1929).
Near the end of the 1800s and into the 1900s, Boosey & Co. “was flourishing, supporting a staff of 100 employees” (Howell, 2016, p. 61). John Dixon was one of their agents and he travelled the world to create find new markets and build contacts, so when James Ord Hume and Besses went on their respective tours it presented an opportunity for John Dixon to go along as well.
Unfortunately, not much is known about John Dixon’s life, but from brief range of articles we can see that he made extensive contacts in the band world (“An Exhibit of Musical Instruments,” 1906; “MUSIC ADJUDICATOR,” 1929; “Personals,” 1903). Writing a long letter to Wright & Round’s Brass Band News on February 1st from New Zealand (published in their April 1st issue), he noted of his experiences,
…In Coolgardie I met John Cox, late of Lassodie, now bandmaster Coolgardie City Band. He has a son a good cornet player. He asked me about a great many Fifeshire bandsmen, and I was able to tell him something about all. He asked me specially to remember him to Mr. James Carmichael of Cowdenbeath, Mr. George Peacock of Fauldhouse, Geordie Pemann and all the Penmans, muckle fat Geordie in particular said he, to Archie Carmichael of Glasgow, and many more. I met an old Bury lad full of the Lancashire love of contesting at Kalgoorlie, where he is bandmaster of the Town Band. Mr. Richard Weber is his name, and a fine fellow he is. He sends his best regards to all his old friends in the Bury, Radcliffe, and Besses districts, not forgetting “Trotter,” whom he says is a “corker.” (He must have meant an uncorker.) At Boulder City I met and heard Mr, Hugh McMahon, the Alex Owen of Australia who took his band 4000 miles to compete at Ballarat and at Bathurst. He is a wonder on the cornet and deserves his title. At Adelaide I found the Loco. Band very good and in charge of an enthusiastic viz., Mr. Charles Allison. […] I have had a very successful tour so far in a business sense, and have established a good many agencies. Give my regards to all old friends and tell them I shall be with them again when the flowers bloom in the spring tra-la. I leave Auckland on February 25th and travel via., Fiji, Honolulu, Canada, New York, and Glasgow.
(Dixon in “Personals,” 1903, p. 7)
It is clear that John Dixon was good at his job and certainly found lots of band friends throughout Australia. His comments on the standards of Australian bands and bandsmen were certainly interesting. It could be debatable whether the sale of Boosey instruments to bands made them any better. However, Boosey (like numerous other instrument companies), milked the fact that certain bands and bandsmen were using their instruments to win competitions – a strong selling point in those days (Boosey and Co., 1919).

James Ord Hume, 1924:
In January 1924 there was much excitement in the band community as it was revealed that James Ord Hume would be making another visit to Australia to adjudicate, twenty-two years after his last visit in 1902 (“MR. J. ORD HUME,” 1924). The Ballarat Star newspaper published a long article full of praise for the work of Ord Hume in 1902 with a brief record of what he did in Australia in his first visit, read out by the President of the South Street Society, Mr Scroucher.
…There is no need for me to tell you who Mr J. Ord Hume is, for with the exception of the very young members of the club, all bandsmen will remember him. He came to Australia some twenty-odd years ago. He judged the South street contest, asked for more tone, told the bandsmen to throw the valve trombone on the scrap heap, gave the prizes to the right persons, and then skipped across to Bathurst. In Bathurst he judged all the musical items from piano right through the list, including all instruments, except, possibly, the bagpipes. He didn’t judge the pipes because there were none to judge. From Bathurst he went to New Zealand, did a lot of work there, created a breeze and skipped back to Sydney, where he judged a big contest. He also did other work, and good work too. Through his criticism and acting on his advice, many bands became better musical organisations. And now, after all these year he is about to visit us again.
(“MR. J. ORD HUME,” 1924)
Part of the rest of the article comprised of a ditty, which will not be written here for the sake of brevity. Needless to say, the ditty highlighted the delight in knowing that Ord Hume was coming back to Ballarat.
Frank Wright also eloquently wrote of the second visit in his memorial article for the British Bandsman in June 1935.
But since those early days a new generation of Australian bandsman had sprung up. A generation to whom the name of J. Ord Hume is no less magical than it was to those enthusiasts of 1901. It is little wonder then, that his second – and last – visit in 1924-5 was hailed as an even greater event than the first.
(Wright, 1935, p. 4)
Given that Ord Hume visited in 1902 and had provided advice to bands on how to improve, Besses toured in 1907 and 1910 and cast a lasting legacy over Australian bands, the fact that Ord Hume visited again in 1924 provides us with expert assessment on which standard Australian bands had reached. We need to only look at his words which were published in an Argus article in October 1924 upon his welcome to Ballarat. This was the only competition Ord Hume was to adjudicate in Australia this year.
Mr. Hume referred to the successes of the Newcastle Band in England, and said that it could rank with the cream of British bands. Australian bands had improved wonderfully, but he could not say the same of the English bands. […] His object in visiting Ballarat was not only to judge, but also to advise. If he could do anything to further raise the standard of band music in Australia it would be done. When in Melbourne on Sunday he had heard the Malvern Tramways Band, and he had been delighted with its excellent tone. It should always be the aim of a brass band to develop a good tone.
(“AUSTRALIAN BANDS.,” 1924)

Ord Hume was always one to make further comments and in 1926 he teamed up with Canadian Lieut. Alfred Edward Zealley to write a book, ‘Famous Bands of the British Empire’. This book was essentially a list of the best bands, military and brass, that they perceived to be the finest of the time. Four Australian bands made the list: New South Wales Lancers band, Malvern Tramways Band, Newcastle Steelworks Band and The Australian Commonwealth Band. It is in the section detailing the exploits of the Malvern Tramways Band thus far that we can find more of the story on Besses and Ord Hume in Australia. What is written here is a perfect response to his prophecy from 1903 at the top of this post.

Conclusion:
There is enough evidence to suggest that the visits of James Ord Hume and the Besses band to Australia were the great catalysts in boosting the standards of Australian bands. It is a fascinating story, and there is much that could have been added as there are always side stories that link into this central theme. It could be argued that there were other influences that were working on Australian bands. Certainly, in the early 1900s, there was a crop of highly skilled bands people coming through the ranks that were gaining notice in the band movement. However, help was provided from these British experts and their legacy, and memory, lives on.
References:
About Trombones. (1902, 28 November). Molong Argus (NSW : 1896 – 1921), 15. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article144160543
AMUSEMENTS : BESSES O’ TH’ BARN BAND : THE BALLARAT SEASON : OPENING PERFORMANCES. (1910, 04 June). Ballarat Star (Vic. : 1865 – 1924), 1. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article216365174
AUSTRALIAN BANDS : GREATLY IMPROVED : Visiting Adjudicator’s View. (1924, 15 October). Argus (Melbourne, Vic. : 1848 – 1957), 22. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article2050652
BALLARAT COMPETITIONS. (1902, 08 November). Adelaide Observer (SA : 1843 – 1904), 36. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article161788993
BAND BANQUET : Howard Function : ANNUAL MEETING. (1933, 21 December). Maryborough Chronicle, Wide Bay and Burnett Advertiser (Qld. : 1860 – 1947), 2. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article149267526
Bathurst Band Contests : A Warm Sort of Judge : His Remarks at Ballarat. (1902, 06 November). Mudgee Guardian and North-Western Representative (NSW : 1890 – 1954), 18. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article157697522
Bathurst Musical and Literary. (1902, 13 November). National Advocate (Bathurst, NSW : 1889 – 1954), 5-6. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article157251693
Besses o’ th’ Barn Band Channel. (2022, 02 January). Besses o’ th’ Barn Polka (1940) [Video (1940 Radio Broadcast)]. YouTube. Retrieved 02 January 2022 from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PE5vkyi1vIg
BESSES O’ TH’ BARN BAND. (1907a, 24 July). Goulburn Herald (NSW : 1881 – 1907), 2. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article100454780
Besses o’ th’ Barn Band. (1907, 09 August). Quiz (Adelaide, SA : 1900 – 1909), 8. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article166338966
BESSES O’ TH’ BARN BAND. (1907b, 06 September). Bendigo Advertiser (Vic. : 1855 – 1918), 5. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article89858023
BESSES O’ TH’ BARN BAND. (1907c, 10 August). Register (Adelaide, SA : 1901 – 1929), 5. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article56528158
Besses o’ th’ Barn Band. (1907). [Photograph]. [13953]. Manchester Digital Music Archive. https://www.mdmarchive.co.uk/artefact/13953/BESSES_O’_TH’_BARN_BAND_PHOTOGRAPH_1907
BESSES O’ TH’ BARN BAND : A NOTABLE CONDUCTOR. (1907d, 25 July). Herald (Melbourne, Vic. : 1861 – 1954), 3. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article243298679
BESSES O’ TH’ BARN BAND : WELCOME TO MELBOURNE. (1907e, 29 July). Argus (Melbourne, Vic. : 1848 – 1957), 7. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article10125983
Boosey and Co. (1919). A Famous Soloist [Advertisement]. The Australian Band News, 12(10), 18.
CHAMPIONSHIP BAND CONTEST : INTERESTING COMPETITIONS. (1902, 29 December). Sydney Morning Herald (NSW : 1842 – 1954), 3. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article14480823
de Korte, J. D. (2018a, 14 October). International band tours of the early 1900’s: bringing music to Australia. Band Blasts from the Past : Anecdotes, Stories and Personalities. https://bandblastsfromthepast.blog/2018/10/14/_international-band-tours-of-the-early-1900s-bringing-music-to-australia/
de Korte, J. D. (2018b, 02 March). William Ryder: The first conductor of the Prahran & Malvern Tramways Employees Band. Band Blasts from the Past : Anecdotes, Stories and Personalities. https://bandblastsfromthepast.blog/2018/03/02/william-ryder-the-first-conductor-of-the-prahran-malvern-tramways-employees-band/
EMPEROR OF CORNET : Some Triumphs of Genius : AUSTRALIA’S BAND MUSIC. (1930, 20 September). Daily News (Perth, WA : 1882 – 1950), 6. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article79474044
An Exhibit of Musical Instruments. (1906, 13 October). Star, 7. https://paperspast.natlib.govt.nz/newspapers/TS19061013.2.94.5
Howell, J. (2016). Boosey & Hawkes: The rise and fall of a wind instrument manufacturing empire (Publication Number 16081) [PhD, City University of London, School of Arts, Department of Creative Practice & Enterprise – Centre for Music Studies]. City Research Online. London, UK. http://openaccess.city.ac.uk/id/eprint/16081
Mr. Alexander Owen : THE GREATEST BRASS BAND CONDUCTOR IN THE WORLD. (1907, 01 July). Evening Telegraph (Charters Towers, Qld. : 1901 – 1921), 4. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article214932270
MR. J. ORD HUME : AN INTERESTING INTERVIEW : WHAT AUSTRALIAN BANDS LACK. (1903, 25 February). Ballarat Star (Vic. : 1865 – 1924), 3. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article208462723
MR. J. ORD HUME : POPULAR WITH BANDSMEN. (1924, 26 January). Ballarat Star (Vic. : 1865 – 1924), 10. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article213955763
Mullen, C. C. (1965). Brass bands have played a prominent part in the history of Victoria. The Victorian Historical Magazine, 36(1), 30-47.
MUSIC ADJUDICATOR : Death of Mr. J. Dixon. (1929, 22 July). News (Adelaide, SA : 1923 – 1954), 2. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article129174877
THE MUSIC OF THE BAND : AUSTRALIA’S FUTURE : CHAT WITH BRITISH EXPERTS. (1910, 12 August). Evening News (Sydney, NSW : 1869 – 1931), 6. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article115252341
Personals. (1903). Wright & Round’s Brass Band News(259), 7. http://usir.salford.ac.uk/id/eprint/45510/
Prestwich, M. (1906). Besses o’ th’ Barn Band [Postcard]. Martin Prestwich, Manchester, United Kingdom.
Quickstep. (1920a, 11 September). Bandsmen’s Gossip : Australia’s Great Soloist. Herald (Melbourne, Vic. : 1861 – 1954), 14. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article242308980
Quickstep. (1920b, 23 October). Bandsmen’s Gossip : Celebrated Conductor. Herald (Melbourne, Vic. : 1861 – 1954), 4. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article242245731
The Royal Besses O’ Th’ Barn Band : The Finest in the World. (1907). [Postcard]. Besses O’ Th’ Barn Band.
Seymour, C. (1994). Adelaide’s Tramway Band. Trolley Wire, 35(4), 3-10. https://www.sydneytramwaymuseum.com.au/members.old/Trolley_Wire/259%20-%20Trolley%20Wire%20-%20Nov%201994.pdf
SOUTH STREET SOCIETY : A SOCIAL FUNCTION : TO MR J. ORD HUME. (1902, 04 November). Ballarat Star (Vic. : 1865 – 1924), 1. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article208361692
SOUTH-STREET COMPETITION’S : Inaugural Concert. (1902, 03 October). Argus (Melbourne, Vic. : 1848 – 1957), 6. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article9062176
Thirst, T. (2006). James Ord Hume 1864-1932 : a friend to all bandsmen : an account of his life and music. Timothy Thirst.
WOULD CAPTURE LONDON : Malvern Band Praised : “CONDUCTOR A GENIUS”. (1922, 30 October). Herald (Melbourne, Vic. : 1861 – 1954), 7. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article243776990
Wright, F. (1935). The late J. ORD HUME : An Appreciation. British Bandsman, 4-5.
Zealley, A. E., & Ord Hume, J. (1926). Famous Bands of the British Empire : Brief Historical Records of the recognized leading Military Bands and Brass Bands in the Empire. J. P. Hull.