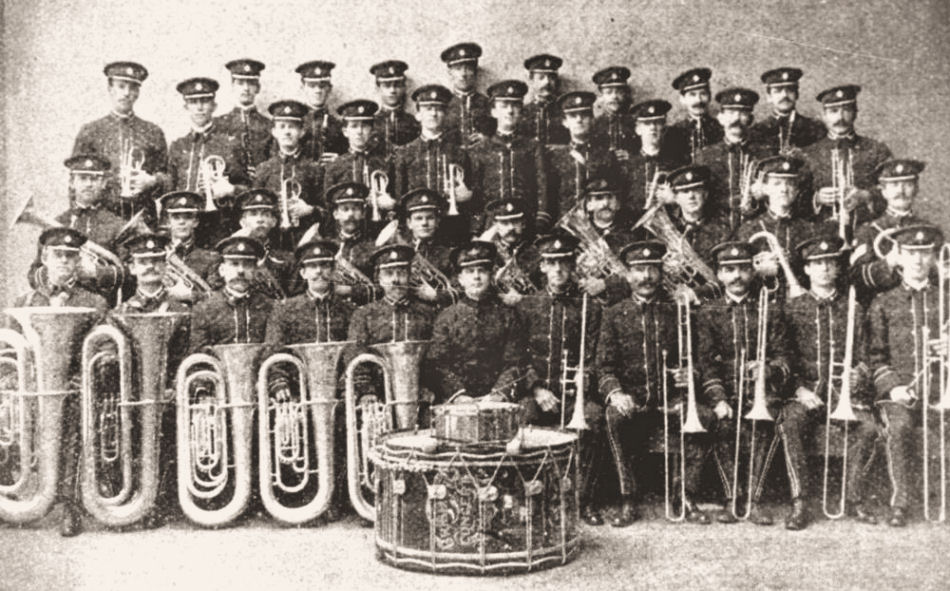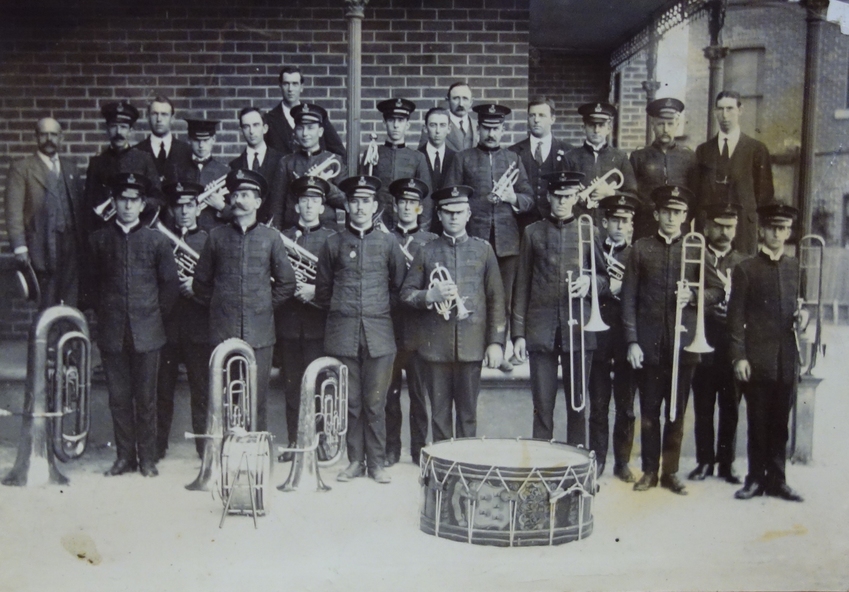
(Source: Victorian Collections: Victorian Bands’ League Archives)
An international band contest may be a feature of the Centenary celebrations. An effort will be made to include one in the 1934 Eisteddfod and Band Contest at Ballarat.
The Grand National Eisteddfod of Australasia has promised its enthusiastic support of the celebrations. Bands contests were resumed last year at the Ballarat competitions after a lapse of eight years, and they proved successful. (“Band Contest For Centenary,” 1933)
Introduction:
The year is 1934 and in Ballarat on the 1st of November, the Royal South Street Eisteddfod band sections are getting underway again. Except this year is a bit different. It is the year of the Victorian and Melbourne Centenary and across Victoria, celebrations and other events are in full swing. The South Street band sections were part of these grand festivities, and all efforts were made to attract bands from across Australia and New Zealand. In addition, the band contest was honoured by the presence of Prince Henry, Duke of Gloucester and The Band of HM Grenadier Guards. The Royal South Street Society band contest, while being the most prestigious, attracted the most attention in the wider band movement. For the bands themselves, there were lots of other events and band contests they were involved in.
Planning for the 1934 Ballarat band contest was extensive and as shown by the quote at the head of this post, the ideas started over eighteen months earlier. Even if the idealism of the organisers was led astray at times. They thought big, but had to accept that economic conditions were not the best as Australia was coming out of the Great Depression. To put on a band contest befitting a visit of royalty was the utmost challenge. Not to mention the scheduling given the extensive touring of the Grenadier Guards Band and the Duke.
With the cooperation many different parties, somehow, everything worked out. This post is mainly about the 1934 South Street band contest, ninety years to the day.
The Centenary:
Officially, the Victorian and Melbourne centenaries marked two historical events; the landing of the Henty family in Portland 1834, and John Batman’s grand pronouncement in 1835 that the Port Philip bay area with the Yarra River at its head would be “the place for a Village” (McCubbin, 2008). However, like any celebration of this nature, there was some curious disagreement over the dates, especially from interstate commentators. An article published in The Adelaide Chronicle newspaper in April 1934 questioned the historical accuracy of the centenary. The article suggested that 1934 was too early as Victoria was officially proclaimed an independent colony in 1851 (“Victoria’s Centenary,” 1934). Or maybe, as the article also suggested, the centenary was thirty-two years too late as 1802 was the year surveyors from New South Wales first explored the country in the vicinity of Port Phillip Bay (“Victoria’s Centenary,” 1934). And there were plenty of other historical events connected with Victoria before 1834 that could have been commemorated. The Victorian Government was probably well aware of these dates and as an article published in The Record newspaper proclaimed:
And now after warring factions have harmonised, the official foundation of Victoria is given as November 19, 1834, when the “Thistle” anchored in Portland Bay: and the centenary of this event is to be taken as the starting point of our Centenary celebrations. (“Victoria’s Centenary.,” 1933)
Nowadays Victoria celebrates an event on the 1st of July each year which marks the day Victoria was officially proclaimed an independent colony from New South Wales (Brown, 2015). Melbourne Day is also recognized on the 30th of August each year which commemorates “the anniversary of the first European settlement in 1835” (Melbourne Day, 2024).
Confusing, isn’t it…
Prince Henry, Duke of Gloucester:
As early as 1932 if newspaper reports are anything to go by, negotiations were underway to bring a member of the Royal Family to Victoria for the Centenary commemorations in 1934. The Scrutineer and Berrima District Press newspaper was one of these and they published a tiny article on the 6th of November 1932.
Victoria’s Centenary will probably be celebrated from October, 1934, to February, 1935. Negotiations are in progress for a Royal visit, and it is almost certain that the British Fleet, which was to have visited Australia in 1933, will postpone the visit to coincide with the celebrations. (“Victoria’s Centenary,” 1932)
By early May 1933, the progress of the negotiations was evident to the extent that it was confirmed a member of the Royal Family would visit in 1934. But which one? The Victorian government initiated the negotiations; however, Canberra was also involved and any Royal that visited would be taken to the national capital as well, and to various places in Australia and New Zealand. Speculation as to which Royal it might be was rife, and as reported by The Herald and several other newspapers, the Royal family member was going to be the Earl of Athlone, the brother of the Queen, or the Duke of Gloucester, the King’s third son (“CENTENARY PLANS TAKE SHAPE,” 1933).
In February 1934, the proposed Royal was mentioned in various newspapers as Prince George and the Royal South Street Society immediately sought to secure a visit to Ballarat by the Prince on the 1st of November so that he could open the famous band sections (“CENTENARY BAND CONTEST,” 1934). The RSSS was concerned that the Prince, according to a tentative itinerary, might be in New South Wales while the contest was taking place.

However, even with the best of plans, circumstances can change overnight, and by May 1934, news broke about a change of Royal, but this did not substantially alter the planning of a Royal visit.
It was announced, in the week-end, that, owing to the strain of the South African tour, Prince George would be unable to fulfil the engagement to come to Australia for the Melbourne Centenary celebrations. Prince Henry, Duke of Gloucester, is to take his place.
The least robust member of the Royal family, Prince George felt the strain of his South African tour before it was finished. It was far heavier than had been expected, and his letters home indicated that he was feeling tired, although delighted at the cordiality of his reception everywhere.
It was consequently considered unwise for a young man of Prince George’s temperament, which is rather highly strung, to undertake a second tour, especially as the Australasian programme was longer and more arduous than the African.
[…]
The Duke of Gloucester is the only one of the King’s sons who has not yet toured the Empire. He fulfilled his duties during his visit to Japan so well that it was felt that he should be given the opportunity to visit Australia, where he would be likely to find so much congenial to his temperament. (“Duke of Gloucester to Come Here for Centenary Celebrations,” 1934)
With a member of a Royal family confirmed, and in all likelihood, the Duke of Gloucester would be in Ballarat on the 1st of November, planning for other parts of the Centenary celebrations and the band contest continued (“CENTENARY BAND CONTEST.,” 1934).

The Duke arrived in Australia in early October and visited Perth, then Adelaide on his way to Melbourne, travelling aboard H.M.S. Sussex which was escorted by elements of the Australian naval fleet (“DEPARTURE OF H.M.S. SUSSEX.,” 1934). Prince Henry disembarked in Melbourne on the 18th of October and was afforded all the military and civic pageantry that Victoria could muster at the time. Below is a short film clip of his arrival and speech on the steps of the Victorian Parliament.
The Band of HM Grenadier Guards:

If the experiences of bringing a member of the Royal family to Ballarat was anything to go by, then securing a visit by one of the finest military bands in the world (at that time) was no less stressful and speculative. Given the planning of the Centenary celebrations were well-underway in 1933, this is when newspapers started reporting that an English military band would be visiting as part of the festivities. The Argus newspaper published a lengthy article in September 1933 that mentioned the Coldstream Guards, and that Victorian band musicians would be eager to hear them play, and be inspired (“COLDSTREAM GUARDS BAND,” 1933). As mentioned in a previous post about this tour, only the Musicians’ Union raised objections to the tour of an English band, a position that was berated by a letter writer to The Herald newspaper (de Korte, 2018b; Musician, 1933). In October, The Age newspaper was a little more speculative – given there are multiple guards’ bands, this article mentioned the bands of the Coldstream Guards, Welsh Guards, or Grenadier Guards as possibilities of touring (“GUARDS’ BAND VISIT.,” 1933).
It was quite a bit later, June 1934, that the Grenadier Guards Band was strongly expected to be the English military band visiting for the Centenary, and that their tour, estimated to cost £10,000 pounds, would also take in provincial towns (“FAMOUS BAND EXPECTED,” 1934). In August, this tour was very much confirmed – one could appreciate the formality of the article published in The Age newspaper.
By special permission of the King, the band of Grenadier Guards is to give a season in Melbourne under the auspices of the Commonwealth and New Zealand Governments and the Centenary Celebrations Council, and Messrs. J. and N. Tait have been entrusted with the management of the tour. The opening concert will be given in the Town Hall on Saturday, 20th October. The band is the premier band of the United Kingdom, and negotiations for this visit have been carried through the Commonwealth High Commissioner in London with the British Government. The band has no fewer than twenty different programmes. Their uniforms of scarlet, blue and gold, with bearskin busbies, should make a fine spectacle. (“Grenadier Guards’ Band.,” 1934)
The Grenadier Guards band duly arrived in Melbourne on the 20th of October and were given a civic reception at the town hall, and a parade up Collins Street led by the Melbourne Fire Brigade Band (“GRENADIER GUARDS BAND HAS WONDERFUL WELCOME.,” 1934). The picture below published in The Age newspaper showing the proceedings, and part of the crowd of 100,000, says it all.

After their welcome in Melbourne and opening concert, the Band of the Grenadier Guards commenced on a country tour of Victoria, such was the interest in their visit – their first tour concert was in Wangaratta on the 22nd of October (“GRENADIER GUARDS BAND.,” 1934). By no coincidence at all, many of the places the band visited intersected with visits of the Duke of Gloucester, including Ballarat on the 1st of November.
Of interest is the back cover of the programme used for this visit which advertises Boosey & Hawkes instruments, and the Australian music retailers that sold them – with a picture of H.M.S. Sussex which was transporting Prince Henry to Australia (Kingtson, 1934).

Programme: Back Cover – The Band of His Majesty’s Grenadier Guards : By Special Permission of the King, 1934. (Source: Jeremy de Korte Collection)
Two of the puzzle pieces for the Royal South Street band contest were now in place. But we must not forget the brass bands that were travelling to South Street for the contest.
Attracting the bands:
It would not be a band contest without the bands, and the Royal South Street Society, conscious of the significance of the 1934 contest, wanted to put on a good show. At the head of this post was the idea that the band contest could be an international contest with the finest bands from around the world travelling to Ballarat to participate (“Band Contest For Centenary,” 1933). Alas, bringing international bands was not to be. Australia was just coming out of the Great Depression and economic conditions were not the best and attracting international bands was probably deemed too expensive (de Korte, 2020). Nevertheless, in June 1933 the Lord Mayor of Melbourne gave his blessing to the band contest in Ballarat, stating,
Ballarat is looked upon as the venue for brass band contests, and I can assure you that during the centenary celebrations it will be recognised as such” said the Lord Mayor of Melbourne (Councillor H. Gengoult Smith) in speaking at a civic welcome at the city hall yesterday. […] In recognition of what Ballarat, through the South Street Society, had done for the encouragement of brass band music, he would give his assurance that the finals of the centenary band contest would be held in Ballarat. (“CENTENARY BAND CONTEST.,” 1933)
The Mayor of Ballarat, Cr. A. J. Darling expressed confidence in January 1934 that arrangements for the official opening of the Centenary band contest were well-underway, as well as confirmation that a member of the Royal family would be attending (“CENTENARY BAND CONTEST.,” 1934). With the Royal South Street Society and the newly formed Victorian Bands’ League working on the particulars of the contest, there was no need to think this was not the case. And in April came the details of the prize money that was on offer, and the announcement that “Mr. Stephen Yorke, conductor of the Australian national military band, will adjudicate.” (“CENTENARY BAND CONTESTS.,” 1934). On a side note, the A.B.C. Military Band was undertaking its own national tour in 1934 – it was a great year to listen to top bands in Australia (de Korte, 2018a).
Individual bands were also starting to make plans to visit Ballarat for the contest. We see that in April, the Mildura Municipal Band (also known as the Sunraysia District Brass Band) announced plans to visit Ballarat to listen to the A grade sections, and then proceed to Melbourne to present a concert in conjunction with the Essendon City Band (“CENTENARY BAND CONTESTS,” 1934). However, their ideas must have changed as they ended up participating in the contest in the C and D grade sections, and achieving equal first prize with the Pleasant Street Boys’ Band in the D grade (Royal South Street Society, 1934c).



Interest in competing was also expressed by bands in New Zealand as the Woolston Brass Band announced its intention to come to Ballarat for the centenary contest (“NEW ZEALAND BAND TO VISIT MELBOURNE.,” 1933). An article published in the Dominion newspaper by the writer, ‘Kneller Hall’, speculated that the Port Nicholson Silver Band was preparing to travel to Ballarat to compete, while also confirming that the famous Woolston Brass Band was going to make the trip over the Tasman (Kneller Hall, 1934). In the end, only one band from New Zealand ended up attending, Woolston, and they were given a civic welcome when they arrived in Ballarat (“BALLARAT AND DISTRICT,” 1934; “PROVINCIAL CITIES AND TOWNS.,” 1934a).

The South Street “Centenary” Band Contest:
With bands arriving in Ballarat, the Duke of Gloucester travelling down by train from Mildura, and the Band of the Grenadier Guards arriving from Bendigo, all was now in place for the opening of the Royal South Street band sections on the 1st of November (“GRENADIER GUARDS BAND.,” 1934; “Sunraysia, Land of Sunshine Greets The Duke,” 1934). Twenty-two bands from Victoria, Tasmania, New South Wales, and New Zealand had entered the South Street contests this year and the list of bands and bandmasters in the official souvenir programme can be viewed below (Royal South Street Society, 1934e).

(Source: Victorian Collections: Victorian Bands’ League Archives)
To have twenty-two bands enter in 1934 was not bad considering that the early thirties were times of upheaval for the Victorian band movement and society in general. In 1931, the Victorian Bands’ League was established having superseded the Victorian Bands’ Association, the Australian economy was recovering after the Great Depression, and the band sections at Royal South Street had resumed in 1932 after an eight year hiatus (de Korte, 2018c, 2020; Royal South Street Society, 1979).
However, it would have been pleasing to see bands from a wide variety of areas coming to South Street. We know that for some bands, like the Phillip Island Brass Band, that they did a considerable amount of fundraising to attend (de Korte, 2019). The line up for bands for the A Grade section represented the best of A grade bands that Victoria had in the day, and having the Woolston Brass Band from Christchurch, N.Z. made the section even more top notch.

The opening day of the band contest was a spectacular affair with the Royal South Street Society having programmed all events down to the minute. According to various newspaper articles, 10,000 people attended the opening day at Ballarat’s City Oval, no doubt drawn to the fact that the Duke of Gloucester would be there to officially open the contest. The souvenir programme outlined the proceedings of the day as can be seen below.

(Source: Victorian Collections: Victorian Bands’ League Archives)
In superb weather, everything proceeded to plan, and the bands did their best to produce a ceremony befitting the occasion (“BAND CONTESTS,” 1934). There was a massed band performance, a demonstration of the quickstep, and the Woolston Brass Band even performed a haka for the Duke after the march past of the bands (“DUKE AT BALLARAT,” 1934). That night, the Band of HM Grenadier Guards performed in a concert which would have inspired the bandsmen and audience (Royal South Street Society, 1934e).
Results for the contests were announced on Saturday 3rd of November with another 10,000 people attending to find out the placings. The full results will not be detailed in this post due to space, but they can be found on the RSSS results database via these links:
- A Grade and B Grade sections (Royal South Street Society, 1934b)
- C Grade section (Royal South Street Society, 1934c)
- D Grade section (Royal South Street Society, 1934d)
The Solo contests were held a day before the band sections on the 31st of October. The results of these can be found on the RSSS database via the link:
- Brass Band Solos (Royal South Street Society, 1934a)
By all accounts, the standard of playing across all sections was brilliant and the adjudicator was very impressed. The A Grade section in particular was a very hard fought affair, but in the end, the Melbourne Fire Brigade Band won the Besson Shield for the third year in a row (Royal South Street Society, 1934a). The Woolston Brass Band from N.Z. suffered some misfortune when one of their cornet players became ill – the other A Grade bands offered them a choice of cornet players to help out – however, they decided to proceed down a player and were happy to achieve third place (“BRILLIANT PLAYING,” 1934; “PROVINCIAL CITIES AND TOWNS.,” 1934b).
The Duke of Gloucester and the Band of the Grenadier Guards did not stay long in Ballarat as they kept up a tight schedule of touring around Victoria and eventually New Zealand. For the bands themselves there were good stories of their visits to Ballarat. The Yallourn and District Band from Gippsland was one band that was very proud of their efforts in the B Grade section where they achieved second place behind the City of Ballarat Band (“YALLOURN NEWS,” 1934). Of interest is that in early 1935, three cornet players from Victorian bands, including cornetist Jack Allan of the City of Ballarat Band, were offered places in the Band of the Grenadier Guards (“Ballarat Bandsman Invited To Join Grenadier Guards,” 1935). It is unclear whether they took up that offer.
The 1934 South Street contest was no doubt an important part of Victoria’s Centenary celebrations, but it was not the only part. There were other important events taking place.
Events after South Street:
11th of November, 1934: Dedication of the Shrine of Remembrance, Melbourne:

For the Duke of Gloucester, he kept up a busy schedule around Victoria. However, his most important engagement was the dedication of Melbourne’s newly completed Shrine of Remembrance. This was a very special occasion which was attended by thousands of veterans, people, and important dignitaries. Bands and other musicians also played an important role, and at the dedication, several Australian Army buglers sounded the Last Post standing behind Royal Australian Navy drummers.
Portland Centenary Band Contest:
The town of Portland in the far south-west of Victoria had an important part to play in Victoria’s centenary celebrations. In turn, they staged their own band contest, albeit on a much smaller scale than the South Street contests which had concluded only two weeks earlier (“BAND CONTESTS.,” 1934). The Portland contest was only attended by bands from Hamilton, Heywood and Mt. Gambier, and there was a pipe band contest held at the same time. The Portland contest was won by the band from Mt. Gambier and the adjudicator was Mr. Percy Jones (“Band Contest Won By Mount Gambier,” 1934).
Melbourne Centenary Band Championship, King’s Birthday weekend, June 1935:
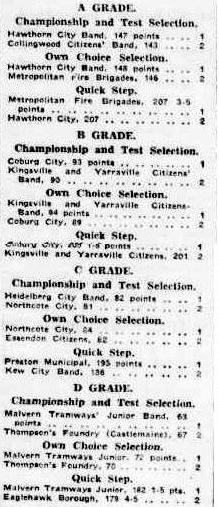
The Victorian centenary celebrations stretched into 1935, and a Melbourne Centenary Band Championship was held at the Exhibition Buildings under the auspices of the Victorian Bands’ League. Like the South Street contests, this was another great event for bands, and twenty-one bands participated, as listed in the article below.

The main attraction of this event was a grand parade from Alexandra Avenue to the Exhibition Buildings and quickstep display on the Exhibition oval (“CENTENARY BAND CONTESTS,” 1935). Again, the A Grade section continued the rivalries between Hawthorn, Melbourne Fire Brigade, Brunswick and Collingwood bands, with Hawthorn taking out the A Grade title (“CENTENARY GALA WEEK.,” 1935). Another celebrated win was that of the Malvern Junior Tramways Band when they won their third D Grade title in a row.
Conclusion:
What an intense period of activity for bands! It is times like these that our bands came to the fore with all the ceremonial and contest activity, as well as local celebrations. No doubt the communities appreciated the efforts and the entertainment. Having a visiting band of the calibre of the Band of the Grenadier Guards made the Centenary celebrations even more special, and it was noted at the time that they were inspiring to local musicians. The prevailing feeling when all was done was one of accomplishment, not just from the cooperation that made this all happen, but from all that understood the significance of the events. It is not every day that a world-class military band and a Duke visits a band contest.
References:
BALLARAT AND DISTRICT. (1934, 08 June). Argus (Melbourne, Vic. : 1848 – 1957), 3. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article10944624
Ballarat Bandsman Invited To Join Grenadier Guards. (1935, 16 January). Sunraysia Daily (Mildura, Vic. : 1920 – 1950), 5. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article265838073
Band Contest For Centenary. (1933, 25 February). Sun News-Pictorial (Melbourne, Vic. : 1922 – 1954; 1956), 4. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article277163952
Band Contest Won By Mount Gambier : Judge’s Eulogistic Comments. (1934, 22 November). Portland Guardian (Vic. : 1876 – 1953), 4. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article64287397
BAND CONTESTS : OPENING AT BALLARAT. (1934, 02 November). Mercury (Hobart, Tas. : 1860 – 1954), 14. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article29165635
BAND CONTESTS : Three Bands Competing. (1934, 19 November). Portland Guardian (Vic. : 1876 – 1953), 5. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article64287383
BRILLIANT PLAYING : Ballarat Band Contest. (1934, 05 November). Evening Post, 9. https://paperspast.natlib.govt.nz/newspapers/EP19341105.2.61
British Pathé. (2014, 13 April). Melbourne Centenary (1934) [Video (Film Clip)]. YouTube. Retrieved 11 October 2024 from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=C4DWQpyx4O0
Brown, S. L. (2015, 01 July). Victoria Day: Was secret gold behind 1851 separation from NSW? ABC Radio Melbourne,6584322. https://www.abc.net.au/news/2015-07-01/victoria-day-was-secret-gold-behind-separation/6584322
CENTENARY BAND CONTEST. (1935, 28 May). Age (Melbourne, Vic. : 1854 – 1954), 11. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article204361353
CENTENARY BAND CONTEST : Arrangements for Opening. (1934, 18 January). Age (Melbourne, Vic. : 1854 – 1954), 9. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article203377704
CENTENARY BAND CONTEST : Finals in Ballarat. (1933, 05 June). Argus (Melbourne, Vic. : 1848 – 1957), 9. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article4740383
CENTENARY BAND CONTEST : Proposed Opening by Prince George. (1934, 23 February). Age (Melbourne, Vic. : 1854 – 1954), 10. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article203376669
CENTENARY BAND CONTESTS. (1935, 31 May). Sunshine Advocate (Vic. : 1924 – 1954), 3. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article74757883
CENTENARY BAND CONTESTS : Mildura Band to Make Trip. (1934, 27 April). Sunraysia Daily (Mildura, Vic. : 1920 – 1950), 4. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article265690603
CENTENARY BAND CONTESTS : South-Street Prize Money. (1934, 13 April). Age (Melbourne, Vic. : 1854 – 1954), 7. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article203842698
CENTENARY GALA WEEK : BAND CONTESTS DECIDED : HAWTHORN CITY WINS A GRADE CHAMPIONSHIP : Malvern Tramway Juniors’ D Grade Treble. (1935, 04 June). Age (Melbourne, Vic. : 1854 – 1954), 10. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article204345548
CENTENARY PLANS TAKE SHAPE : Pageants, Exhibitions And Shrine Dedication : BIG MILITARY TATTOO. (1933, 11 May). Herald (Melbourne, Vic. : 1861 – 1954), 5. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article243112151
COLDSTREAM GUARDS BAND : Victorian Bandsmen Eager For Visit. (1933, 01 September). Argus (Melbourne, Vic. : 1848 – 1957), 8. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article11688130
de Korte, J. D. (2018a, 12 July). The A.B.C. Military Band: an ensemble of the times. Band Blasts from the Past: Anecdotes, Stories and Personalities. https://bandblastsfromthepast.blog/2018/07/12/the-a-b-c-military-band-an-ensemble-of-the-times/
de Korte, J. D. (2018b, 14 October). International band tours of the early 1900’s: bringing music to Australia. Band Blasts from the Past: Anecdotes, Stories and Personalities. https://bandblastsfromthepast.blog/2018/10/14/_international-band-tours-of-the-early-1900s-bringing-music-to-australia/
de Korte, J. D. (2018c, 15 March). The politics of affiliation: The Victorian Bands’ Association to the Victorian Bands’ League. Band Blasts from the Past: Anecdotes, Stories and Personalities. https://bandblastsfromthepast.blog/2018/03/15/the-politics-of-affiliation-victorian-bands-association-to-the-victorian-bands-league/
de Korte, J. D. (2019, 31 January). Bands on Australian islands: unique challenges in unique environments. Band Blasts from the Past: Anecdotes, Stories and Personalities. https://bandblastsfromthepast.blog/2019/01/31/bands-on-australian-islands-unique-challenges-in-unique-environments/
de Korte, J. D. (2020, 18 October). Testing times: the resilience of Australian bands during the Great Depression. Band Blasts from the Past: Anecdotes, Stories and Personalities. https://bandblastsfromthepast.blog/2020/10/18/testing-times-the-resilience-of-australian-bands-during-the-great-depression/
DEPARTURE OF H.M.S. SUSSEX. (1934, 09 October). West Australian (Perth, WA : 1879 – 1954), 17. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article32803514
DUKE AT BALLARAT : AMONG THE BANDS : A WOOLSTON HAKA. (1934, 02 November). Evening Post, 10. https://paperspast.natlib.govt.nz/newspapers/EP19341102.2.102.1
Duke of Gloucester to Come Here for Centenary Celebrations : AFRICAN TOUR TIRED PRINCE GEORGE. (1934, 05 May). Weekly Times (Melbourne, Vic. : 1869 – 1954), 5. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article223836381
FAMOUS BAND EXPECTED : Grenadier Guards for Centenary. (1934, 05 June). Herald (Melbourne, Vic. : 1861 – 1954), 1. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article243175540
GRENADIER GUARDS BAND. (1934, 25 October). Great Southern Advocate (Korumburra, Vic. : 1889 – 1906, 1914 – 1940), 5. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article255918717
GRENADIER GUARDS BAND HAS WONDERFUL WELCOME. (1934, 22 October). Age (Melbourne, Vic. : 1854 – 1954), 15. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article205884483
Grenadier Guards’ Band. (1934, 27 August). Age (Melbourne, Vic. : 1854 – 1954), 13. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article205524735
GUARDS’ BAND VISIT : Centenary Tour Almost Certain. (1933, 10 October). Age (Melbourne, Vic. : 1854 – 1954), 8. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article205104515
Kingtson, C. (Ed.). (1934). Grenadier Guards Band : Australia and New Zealand 1934-5 : By Special Permission of His Majesty the King : Official Souvenir : Tour under the Auspices of the Commonwealth Government and the New Zealand Government : In associaion with the Cenenary Celebrations Council of Victoria [Printed programme]. Grenadier Guards Band.
Kneller Hall. (1934, 27 July). THE BANDS : News and Views : WELLINGTON AND BALLARAT. Dominion, 13. https://paperspast.natlib.govt.nz/newspapers/DOM19340727.2.98
McCubbin, M. (2008). Centenary. In eMelbourne: the city past & present (pp. EM00316b). https://www.emelbourne.net.au/biogs/EM00316b.htm: The University of Melbourne, School of Historical & Philosophical Studies.
Melbourne Day. (2024). More marvellous than ever: FAQs: What is Melbourne Day? Melbourne Day: 30th August. Retrieved 26 October 2024 from https://www.melbourneday.com.au/about.html
Mildura & District Band, 1930s. (1930). [Photograph]. [phot6314]. The Internet Bandsman Everything Within, Vintage Brass Band Pictures – Australia. http://www.ibew.org.uk/vbbp-oz.html
Musician. (1933, 11 September). GUARDS’ BAND VISIT. Herald (Melbourne, Vic. : 1861 – 1954), 6. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article243423748
NEW ZEALAND BAND TO VISIT MELBOURNE. (1933, 13 October). Telegraph (Brisbane, Qld. : 1872 – 1947), 27. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article180593124
Phillip Island Brass Band, 1932. (1932). [Photograph]. [phot16005]. The Internet Bandsman Everything Within, Vintage Brass Band Pictures – Australia. http://www.ibew.org.uk/vbbp-oz.html
Pleasant Street School Band, Ballarat, 1933. (1933). [Photograph]. [phot20817]. The Internet Bandsman Everything Within, Vintage Brass Band Pictures – Australia. http://www.ibew.org.uk/vbbp-oz.html
PROVINCIAL CITIES AND TOWNS : BALLARAT. (1934a, 29 October). Age (Melbourne, Vic. : 1854 – 1954), 13. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article205882825
PROVINCIAL CITIES AND TOWNS : BALLARAT. (1934, 05 November). Age (Melbourne, Vic. : 1854 – 1954), 12. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article205083970
Royal South Street Society. (1934a). 1934-10-31 Brass Band Solos : Held at the A.N.A. Hall, Camp Street [Eisteddfod Results]. Royal South Street Society Results Database. https://results.royalsouthstreet.com.au/results/1934-10-31-brass-band-solos
Royal South Street Society. (1934b). 1934-11-01 Brass Band Contests : Held at City Oval : Grand Champion Centenary Band Contests [Eisteddfod Results]. Royal South Street Society Results Database. https://results.royalsouthstreet.com.au/results/1934-11-01-brass-band-contests
Royal South Street Society. (1934c). 1934-11-02 Brass Band Contests : Held at City Oval [Eisteddfod Results]. Royal South Street Society Results Database. https://results.royalsouthstreet.com.au/results/1934-11-02-brass-band-contests
Royal South Street Society. (1934d). 1934-11-03 Brass Band Contests : Held at City Oval [Eisteddfod Results]. Royal South Street Society Results Database. https://results.royalsouthstreet.com.au/results/1934-11-03-brass-band-contests
Royal South Street Society. (1934e). [South Street “Centenary” : Brass Band Contest : A, B, C and D Grades]. In S09 – Programs (Printed programme ed., pp. 14). Ballarat, Victoria https://victoriancollections.net.au/items/5d425e0c21ea6b1a84382033: Victorian Bands’ League Archive.
Royal South Street Society. (1979). Royal South Street Society : The First One Hundred Years. Royal South Street Society.
ShrineMelbourne. (2013, 09 January). The Dedication of the Shrine of Remembrance – Remembrance Day 11 November 1934 [Video (Film Clip)]. YouTube. Retrieved 26 October 2024 from https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jHcaXEpVdRA
Sunraysia, Land of Sunshine Greets The Duke : Prince Henry Is Our First Royal Guest. (1934, 31 October). Sunraysia Daily (Mildura, Vic. : 1920 – 1950), 21. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article265829018
The Shrine of Remembrance Trustees. (1934). The National War Memorial of Victoria : Aerial View of Dedication Ceremony [Postcard]. [No. 3]. The Shrine of Remembrance Trustees, Great Britain.
To Visit Australia. (1934, 13 October). Dominion, 13. https://paperspast.natlib.govt.nz/newspapers/DOM19341013.2.116.5
Victoria’s Centenary. (1932, 06 November). Scrutineer and Berrima District Press (NSW : 1892 – 1948), 4. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article125232791
Victoria’s Centenary. (1933, 04 November). Record (Emerald Hill, Vic. : 1881 – 1954), 2. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article164468392
Victoria’s Centenary. (1934, 12 April). Chronicle (Adelaide, SA : 1895 – 1954), 39. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article92354462
VISIT TO BALLARAT : Desired for Band Competition. (1934, 01 March). Age (Melbourne, Vic. : 1854 – 1954), 10. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article203834255
YALLOURN NEWS : Yallourn Band. (1934, 08 November). Morwell Advertiser (Morwell, Vic. : 1888 – 1954), 9. http://nla.gov.au/nla.news-article71564079





































